| Structure Identification: |
| Phytochemistry. 2010 Oct;71(14-15):1690-4. | | Biosynthesis of the iridoid glucoside, lamalbid, in Lamium barbatum.[Pubmed: 20656306] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The biosynthesis of the iridoid glucoside Lamalbid in Lamium barbatum, a plant species in the Lamiaceae, was investigated by administrating (13)C-labeled intermediates of MVA and MEP pathways, respectively. The results demonstrated that [3,4,5-(13)C(3)]1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate could be incorporated into Lamalbid, whereas the incorporation of [2-(13)C(1)]mevalonolactone was not observed.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on the (13)C labeling pattern of Lamalbid and the incorporation data, we deduce that the iridoid glucoside in L. barbatum is biosynthesized through the MEP pathway, whereas the classic MVA pathway is not utilized. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1999 Jan;24(1):40-1, 64. | | Iridoid glycosides from Pedicula dicora Franch.[Pubmed: 12078153] | To study the components in the root of Pedicula dicora.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Column chromatography with silica gel and polyamide was employed for the isolation and purification of ingredients. The structures were elucidated by spectral method.
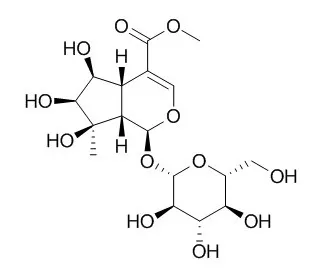
Three iridoid glycosides were obtained and elucidated as mussaenoside, shanzhiside methyl ester and Lamalbid.
CONCLUSIONS:
All the three compounds were separated from P. dicora for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)