| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 1999, 47(3):1223. | | Lipid, polyamide, and flavonol phagostimulants for adult western corn rootworm from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) pollen.[Pubmed: 10552441] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
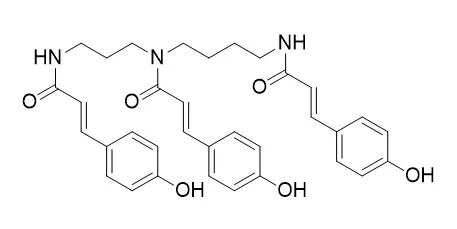
Adult Diabroticites including western corn rootworm (WCR), Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte, consume pollen of corn, squash, sunflower, and other species. Short-chain neutral amino acids in methanol-water extracts of pollen have been previously identified in our laboratory as strong phagostimulants for Diabrotica. Bioassay-driven fractionation was used to characterize the interacting lipid and midpolarity phagostimulants for adult WCR in Giant Gray Stripe sunflower, Helianthus annuus L., pollen. Lipids rich in omega3-linolenic acid including triglycerides, free fatty acids, phosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidic acids, and phosphatidylcholines were highly phagostimulatory. Other important phagostimulatory components included a hydroxycinnamic acid-polyamine amide, N(1),N(5),N(10)-tri[(E)-p-coumaroyl]spermidine(N1,N5,N10-(E)-tri-p-coumaroylspermidine), and a flavonol, quercetin beta-3-O-glucoside.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structural characteristics of these phagoactive compounds and their role in the pollinivory specialization of rootworm beetles are discussed. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)