| In vitro: |
| Phytother Res. 2017 Jul;31(7):1072-1077. | | Nepetoidin B, a Natural Product, Inhibits LPS-stimulated Nitric Oxide Production via Modulation of iNOS Mediated by NF-κB/MKP-5 Pathways.[Pubmed: 28504466] | Previous reports showed that Nepetoidin B (NTB), a natural product isolated from many herbs, has anti-fungal and anti-bacterial effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the antiinflammatory effect of NTB was investigated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. The cytotoxic effect of NTB and LPS was determined by MTT assay. The nitric oxide (NO) production was detected by Griess assay. The TNF-α and IL-6 levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. Protein expressions were tested by western blotting. The transcription activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was detected by luciferase assay. Immunofluorescence assay was used to observe the visualization of NF-κB/p65 nuclear translocation. NTB and LPS showed no obvious cytotoxic effect on RAW 264.7 cells. NTB remarkably inhibited LPS-induced NO and TNF-α secretion in a concentration-dependent manner while showed no significant effect on IL-6 secretion. NTB inhibited LPS-induced iNOS protein expression and transcription activity without affecting cyclooxygenase-2. Furthermore, NTB suppressed LPS-stimulated NF-κB/p65 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. In addition, NTB significantly inhibited LPS-induced phosphorylation of JNK1/2 and p38MAPK without affecting ERK1/2. LPS-induced inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-5 (MKP-5) was completely reversed by NTB.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, these results suggested that NTB inhibited LPS-stimulated NO production possibly via modulation of iNOS mediated by MKP-5/NF-κB pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. | | Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013: 460613. | | Antileishmanial Phenylpropanoids from the Leaves of Hyptis pectinata (L.) Poit.[Pubmed: 23983783] | Hyptis pectinata, popularly known in Brazil as "sambacaitá" or "canudinho," is an aromatic shrub largely grown in the northeast of Brazil. The leaves and bark are used in an infusion for the treatment of throat and skin inflammations, bacterial infections, pain, and cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
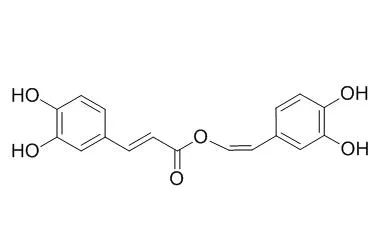
Analogues of rosmarinic acid and flavonoids were obtained from the leaves of Hyptis pectinata and consisted of two new compounds, sambacaitaric acid (1) and 3-O-methyl-sambacaitaric acid (2), and nine known compounds, rosmarinic acid (3), 3-O-methyl-rosmarinic acid (4), ethyl caffeate (5), nepetoidin A (6), Nepetoidin B (7), cirsiliol (8), circimaritin (9), 7-O-methylluteolin (10), and genkwanin (11). The structures of these compounds were determined by spectroscopic methods. Compounds 1-5, and 7 were evaluated in vitro against the promastigote form of L. braziliensis, and the ethanol extract. The hexane, ethyl acetate, and methanol-water fractions were also evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
The EtOH extract, the hexane extract, EtOAc, MeOH:H2O fractions; and compounds 1, 2 and 4 exhibited antileishmanial activity, and compound 1 was as potent as pentamidine. In contrast, compounds 3, 5, and 7 did not present activity against the promastigote form of L. braziliensis below 100 μM. To our knowledge, compounds 1 and 2 are being described for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)