| In vitro: |
| Mar Drugs. 2014 Jun 30;12(7):3970-81. | | Indole diterpenoids and isocoumarin from the fungus, Aspergillus flavus, isolated from the prawn, Penaeus vannamei.[Pubmed: 24983640] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
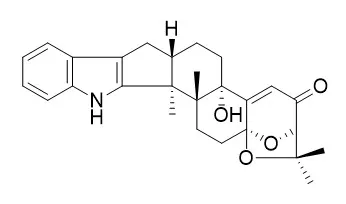
Two new indole-diterpenoids (1 and 2) and a new isocoumarin (3), along with the known β-aflatrem (4), Paspalinine (5), leporin B (6), α-cyclopiazonic acid (7), iso-α-cyclopiazonic acid (8), ditryptophenaline (9), aflatoxin B1 (10), 7-O-acetylkojic acid (11) and kojic acid (12), were isolated from the fermentation broth of the marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus flavus OUCMDZ-2205. The structures of Compounds 1-12 were elucidated by spectroscopic analyses, quantum ECD calculations and the chemical method. New
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 1 exhibited antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus with a MIC value of 20.5 μM.
Both new Compounds 1 and 2 could arrest the A549 cell cycle in the S phase at a concentration of 10 μM. Compound 1 showed PKC-beta inhibition with an IC50 value of 15.6 μM. In addition, the absolute configurations of the known compounds, 4-6 and leporin A (6a), were also determined for the first time. | | Life Sci. 1987 Nov 9;41(19):2207-14. | | Action of tremorgenic mycotoxins on GABAA receptor.[Pubmed: 2444852] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effects of four tremorgenic and one nontremorgenic mycotoxins were studied on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor binding and function in rat brain and on binding of a voltage-operated Cl- channel in Torpedo electric organ. None of the mycotoxins had significant effect on [3H]muscimol or [3H]flunitrazepam binding to the GABAA receptor. However, only the four tremorgenic mycotoxins inhibited GABA-induced 36Cl- influx and [35S] t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate [( 35S]TBPS) binding in rat brain membranes, while the nontremorgenic verruculotoxin had no effect. Inhibition of [35S]TBPS binding by Paspalinine was non-competitive. This suggests that tremorgenic mycotoxins inhibit GABAA receptor function by binding close to the receptor's Cl- channel. On the voltage-operated Cl- channel, only high concentrations of verruculogen and verruculotoxin caused significant inhibition of the channel's binding of [35S]TBPS.
CONCLUSIONS:
The data suggest that the tremorgenic action of these mycotoxins may be due in part to their inhibition of GABAA receptor function. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)