| In vitro: |
| Planta Med. 1998 Feb;64(1):72-4. | | Pinusolidic acid: a platelet-activating factor inhibitor from Biota orientalis.[Pubmed: 9491770 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The water extract of Biota orientalis showed a potent inhibitory effect on platelet activating factor (PAF) binding to rabbit platelets using [3H]PAF as a ligand in our previous screening studies for Korean medicinal antagonists by the activity-guided purification studies. Another active compound, compound 1 (IC50 = 2.3 x 10(-5) M, 7.48 +/- 2.11 micrograms/ml, n = 4) was isolated from the title plant.
CONCLUSIONS:
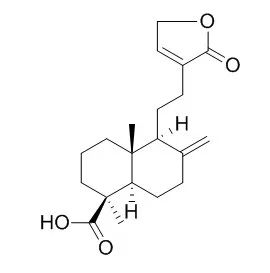
The chemical structure of compound 1 was elucidated as Pinusolidic acid by chemical and spectrometric analyses. | | J Nat Prod. 2006 Apr;69(4):689-91. | | Neuroprotective diterpenes from the fruiting body of Antrodia camphorata.[Pubmed: 16643055] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new compounds, 19-hydroxylabda-8(17)-en-16,15-olide (1), 3beta,19-dihydroxylabda-8(17),11E-dien-16,15-olide (2), and 13-epi-3beta,19-dihydroxylabda-8(17),11E-dien-16,15-olide (3), together with four known compounds, 19-hydroxylabda-8(17),13-dien-16,15-olide (4), 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide (5), 14-deoxyandrographolide, and Pinusolidic acid, were isolated from the fruiting bodies of Antrodia camphorata. The structures of compounds 1-3 were elucidated by the analysis of their spectroscopic data.
CONCLUSIONS:
The in vitro neuroprotective activity of all compounds was evaluated, and compounds 1-5 protected neurons from Abeta damage by 39.2, 35.0, 36.7, 30.6, and 27.0%, respectively, at concentrations between 5 and 20 microM. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)