| Cell Research: |
| Pharm Biol. 2016 Oct;54(10):2044-9. | | Cytotoxic activity and chemical constituents of Anthemis mirheydari.[Pubmed: 26864903 ] | The genus Anthemis L. (Asteraceae) comprises about 195 species which are widely used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries. Anthemis mirheydari Iranshar, an endemic plant from Iran, was investigated for its cytotoxic properties and chemical constituents.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
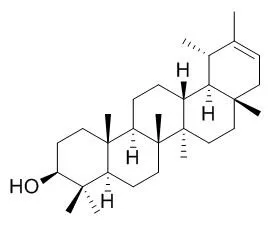
The whole parts of the plant (320 g) were extracted by dichloromethane and methanol for four days, successively. The cytotoxic activity of both dichloromethane and methanol extracts were assayed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide colorimetric methods against three human cancer cell lines including LS180, MCF-7 and MOLT-4. Different concentrations (10-100 μg/mL) of the plant extracts were tested to obtain IC50 values. The dichloromethane extract of A. mirheydari was subjected to silica gel-column and thin layer chromatography for purification of its chemical constituents and the isolated compounds were further tested against MOLT-4 cells. The structures of the pure compounds were elucidated using different spectral data including nuclear magnetic resonance and electron impact mass spectra. The IC50 values of the dichloromethane extract were 30.8 ± 6.7, 25.2 ± 6.5 and 8.6 ± 1.1 μg/mL (means ± standard error) for the above-mentioned cell lines, respectively. Two triterpenoids, taraxasterol (1) and Pseudotaraxasterol (2), one sterol, β-sitosterol (3) and one coumarin, 7-methoxycoumarin (4) were isolated from the extract. The IC50 of the mixture of compounds 1 and 2 as well as compounds 3 and 4 were higher (>100 μM) than that reported for the dichloromethane extract against MOLT-4 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The dichloromethane extract was the most active one among the tested material. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;37(7):937-40. | | [Chemical constituents of Eupatorium lindleyanum].[Pubmed: 22792793] | To study chemical constituents of Eupatorium lindleyanum.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ethyl acetate extractive fractions were separated with silica gel and Sephadex LH-20 by column chromatography, and their structures were identified on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and chemical evidence. Sixteen compounds were separated and identified as scopoletin (1), 6, 7-dimethylesculetin (2), nepetin (3), eupatrin (4), luteolin (5), isoquerecitrin (6), jaceosidin (7), quceritin (8), kaempferol (9), rutin (10), cirsiliol (11), taraxasterylacetate (12), pseudotaraxasteryl acetate (13), Pseudotaraxasterol (14), butanoic acid (15) and n-hexadecanoic acid (16).
CONCLUSIONS:
Of them, compounds 1-6 and 11, 13 and 15 were separated from this plant for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)