| In vitro: |
| Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(20):2322-30. | | In vitro, in vivo and in silico analysis of the anticancer and estrogen-like activity of guava leaf extracts.[Pubmed: 24438525] | Anticancer drug research based on natural compounds enabled the discovery of many drugs currently used in cancer therapy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we report the in vitro, in vivo and in silico anticancer and estrogen-like activity of Psidium guajava L. (guava) extracts and enriched mixture containing the meroterpenes guajadial, Psidial A and psiguadial A and B. All samples were evaluated in vitro for anticancer activity against nine human cancer lines: K562 (leukemia), MCF7 (breast), NCI/ADR-RES (resistant ovarian cancer), NCI-H460 (lung), UACC-62 (melanoma), PC-3 (prostate), HT-29 (colon), OVCAR-3 (ovarian) and 786-0 (kidney). Psidium guajava's active compounds displayed similar physicochemical properties to estradiol and tamoxifen, as in silico molecular docking studies demonstrated that they fit into the estrogen receptors (ERs). The meroterpene-enriched fraction was also evaluated in vivo in a Solid Ehrlich murine breast adenocarcinoma model, and showed to be highly effective in inhibiting tumor growth, also demonstrating uterus increase in comparison to negative controls.
CONCLUSIONS:
The ability of guajadial, Psidial A and psiguadials A and B to reduce tumor growth and stimulate uterus proliferation, as well as their in silico docking similarity to tamoxifen, suggest that these compounds may act as Selective Estrogen Receptors Modulators (SERMs), therefore holding significant potential for anticancer therapy. | | Org Lett. 2010 Nov 5;12(21):5040-3. | | Psiguadials A and B, two novel meroterpenoids with unusual skeletons from the leaves of Psidium guajava.[Pubmed: 20929258] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
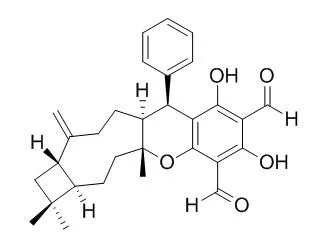
Psiguadials A (1) and B (2), two novel sesquiterpenoid-diphenylmethane meroterpenoids with unusual skeletons, along with a pair of known epimers, Psidial A (3) and guajadial (4), were isolated from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Their structures with absolute configurations were elucidated by means of NMR, X-ray diffraction, and quantum chemical CD calculation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1, 2, and 4 exhibited potent inhibitory effects on the growth of human hepatoma cells. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)