| In vitro: |
| J Nat Prod. 2008 Feb;71(2):212-7. | | Neolignans, a coumarinolignan, lignan derivatives, and a chromene: anti-inflammatory constituents from Zanthoxylum avicennae.[Pubmed: 18211005 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eight new compounds, including four new neolignans, (7' S,8' S)-bilagrewin ( 1), (7' S,8' S)-5-demethoxybilagrewin ( 2), (7' S,8' S)-5- O-demethyl-4'- O-methylbilagrewin ( 3), and (7' S,8' S)-nocomtal ( 4), a new coumarinolignan, (7' S,8' S)-4'- O-methylcleomiscosin D ( 5), two new lignan derivatives, (+)-9'- O-( Z)-feruloyl-5,5'-dimethoxylariciresinol ( 6) and (+)-9'- O-( E)-feruloyl-5,5'-dimethoxylariciresinol ( 7), and a new chromene, ( E)-3-(2,2-dimethyl-2 H-chromen-6-yl)prop-2-enal ( 8), have been isolated from the stem wood of Zanthoxylum avicennae, together with 18 known compounds ( 9- 26). The structures of these new compounds were determined through spectroscopic and MS analyses.
CONCLUSIONS:
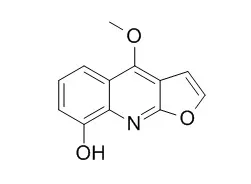
(7' S,8' S)-4'- O-Methylcleomiscosin D ( 5), cleomiscosin D ( 9), skimmianine ( 18), Robustine ( 19), and integrifoliolin ( 23) exhibited inhibition (IC 50 < or = 18.19 microM) of superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils in response to formyl- l-methionyl- l-leucyl- l-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (FMLP/CB). In addition, skimmianine ( 18) inhibited FMLP/CB-induced elastase release with an IC 50 value of 19.15 +/- 0.66 microM. | | Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Jun;28(6):675-9. | | Inhibitory effects of furoquinoline alkaloids from Melicope confusa and Dictamnus albus against human phosphodiesterase 5 (hPDE5A) in vitro.[Pubmed: 16042076] | Eight furoquinoline alkaloids were purified from two plants belonging to the Rutaceae family. Kokusaginine, skimmianine, evolitrine, and confusameline were purified from Melicope confusa, and haplopine, Robustine, dictamine, and gamma-fagarine from Dictamnus albus.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the eight furoquinoline alkaloids were examined for inhibitory potency against human phosphodiesterase 5 (hPDE5A) in vitro. DNA encoding the catalytic domain of human PDE5A was amplified from the mRNA of T24 cells by RT-PCR and was fused to GST in an expression vector. GST-tagged PDE5A was then purified by glutathione affinity chromatography and used in inhibition assays. Of the eight alkaloids, gamma-fagarine was the most potent inhibitor of PDE5A, and its single methoxy group at the C-8 position was shown to be critical for inhibitory activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results clearly illustrate the relationship between PDE5A inhibition and the methoxy group position in furoquinoline alkaloids. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)