| Animal Research: |
| J Med Food. 2004 Winter;7(4):436-41. | | Anti-hepatotoxic effects of Rosa rugosa root and its compound, rosamultin, in rats intoxicated with bromobenzene.[Pubmed: 15671686 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effects of a methanol extract of Rosa rugosa root and its triterpenoid glycoside, Rosamultin, on hepatic lipid peroxidation and drug-metabolizing enzymes were investigated in rats treated with bromobenzene.
The methanol extract of R. rugosa root reduced the activities of aminopyrine N-demethylase and aniline hydroxylase, which had been increased by bromobenzene, but Rosamultin did not affect the activities of the two enzymes. Both the methanol extract and Rosamultin restored the activity of epoxide hydrolase, which had also been decreased by bromobenzene. Hepatic glutathione concentrations were lowered and hepatic lipid peroxides were increased in rats intoxicated with bromobenzene. The hepatic lipid peroxidation induced by bromobenzene was prevented with the methanol extract and Rosamultin. However, the decrease in glutathione was not altered by the methanol extract of R. rugosa.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the extract of R. rugosa and its compound, Rosamultin, may protect against bromobenzene-induced hepatotoxicity through, at least in part, enhanced activity of epoxide hydrolase. Antioxidant properties may contribute to the protection of R. rugosa against bromobenzene-induced hepatotoxicity. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
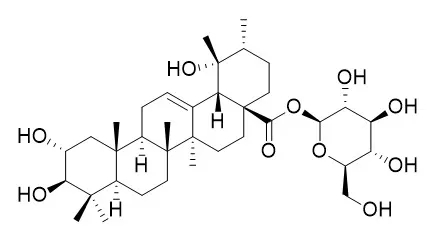
| Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;41(3):451-455 | | Chemical constituents from medical and edible plants of Rosa roxburghii.[Pubmed: 28868863] | Rosa roxburghii, a kind of the medical and edible plants belonging to the Rosaceae family, is widely distributed in the southwest districts of China, especially Guizhou province. Now, by reason of the extensive bioactivities, the plant is widely used in the field of food, health product, drug, and so on.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the course of our continuing search for the bioactive constituents, thirteen compounds were isolated from R. roxburghii, and their structures were determined on the basis of physicochemical property, spectroscopic data and comparison with the literatures, as 2-oxo pomolic acid(1), 1β-hydroxyeuscaphic acid(2), euscaphic acid(3), arjunic acid(4), tormentic acid(5), kaiiichigeside F1(6),
Rosamultin(7), arjunetin(8), 2ɑ, 3ɑ, 19ɑ-trihydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside(9), 2α, 3α, 19α, 24-tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic-acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester(10), pyrogallic acid (11), daucosterol(12), and 1, 2-decanediol(13).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 9 and 10 were firstly obtained from Rosaceae family, and compounds 1,4,5,9-11,13 were isolated from this plant for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)