| In vitro: |
| Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Nov 1;440(4):515-20. | | Specific inhibition of hepatitis C virus entry into host hepatocytes by fungi-derived sulochrin and its derivatives.[Pubmed: 24099774 ] | Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a major causative agent of hepatocellular carcinoma. Although various classes of anti-HCV agents have been under clinical development, most of these agents target RNA replication in the HCV life cycle.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To achieve a more effective multidrug treatment, the development of new, less expensive anti-HCV agents that target a different step in the HCV life cycle is needed. We prepared an in-house natural product library consisting of compounds derived from fungal strains isolated from seaweeds, mosses, and other plants. A cell-based functional screening of the library identified Sulochrin as a compound that decreased HCV infectivity in a multi-round HCV infection assay. Sulochrin inhibited HCV infection in a dose-dependent manner without any apparent cytotoxicity up to 50 μM. HCV pseudoparticle and trans-complemented particle assays suggested that this compound inhibited the entry step in the HCV life cycle.
CONCLUSIONS:
Sulochrin showed anti-HCV activities to multiple HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, and 2a. Co-treatment of Sulochrin with interferon or a protease inhibitor telaprevir synergistically augmented their anti-HCV effects. | | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1983 Dec;31(12):4543-8. | | Studies on metabolites produced by Aspergillus terreus var. aureus. I. Chemical structures and antimicrobial activities of metabolites isolated from culture broth[Reference: WebLink] |
A fungus which was identified as Aspergillus terreus var. aureus showed antifungal and antibacterial activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
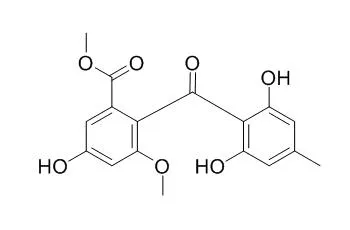
Through the investigation of its metabolites, six compounds (1-6) were isolated; emodin (1), dihydrogeodin (2), questin (3), Sulochrin (5), the new metabolite 2-(3-chloro-4-methyl-γ-resorcyloyl)-5-hydroxy-m-anisic acid methyl ester (4), which is a monochloro derivative of Sulochrin (5), and compound (6), the chemical structure of which has not yet been clarified.
CONCLUSIONS:
Dihydrogeodin (2), Sulochrin (5), 4 and 6 showed antifungal and antibacterial activities, and 6 has especially strong antifungal activity towards Trichophyton mentagrophytes. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)