| Animal Research: |
| Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:542385. | | Evaluation of anticonvulsant, sedative, anxiolytic, and phytochemical profile of the methanol extract from the aerial parts of Swertia corymbosa (Griseb.) wight ex C.B. Clarke.[Pubmed: 24877112] | The objective of the present study was to evaluate the anxiolytic, antidepressant, and anticonvulsant activity of the methanolic extract of Swertia corymbosa (SCMeOH).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After acute toxicity test, oral treatment with SCMeOH at doses of 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg behavioral models of open field, elevated-plus-maze, actophotometer, rotarod, pentylenetetrazole, isoniazid, and maximal electroshock induced seizure models were utilized. In open field test, SCMeOH (125, 250, and 500 mg/kg) (P < 0.01, P < 0.001) increased the number of rearings. However, the number of central motor and ambulation (P < 0.01, P < 0.001) were reduced. Likewise, the number of entries and the time spent in open arm were increased while the number of locomotion was decreased (P < 0.001) in elevated-plus-maze and actophotometer test, respectively. SCMeOH (125-500 mg/kg) protected the mice against the pentylenetetrazole and isoniazid induced convulsions; it causes significant (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001) dose dependent increase in latency of convulsion.
CONCLUSIONS:
Treatment with SCMeOH reduced the duration of the tonic hind limb extension induced by electroshock.
Two major compounds such as gentiopicroside and Swertianin were analyzed by HPLC system. | | International Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2013, 5(3):523-529. | | Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and antinoceceptive activity of xanthones from Swertia Corymbosa (Griseb.) Wight ex C.B. Clarke[Reference: WebLink] | This study was designed to investigate analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of the xanthones isolated from Swertia corymbosa.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
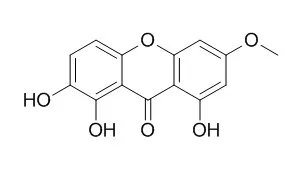
Aerial part of Swertia corymbosa was extracted with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate, further subjected to chromatographic separation for isolation of xanthones. Structures of isolated xanthones were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. Anti-inflammatory (carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat), analgesic action was estimated in mice using the acetic acid-induced writhing test and the hot-plate method and the acute oral toxicity study in mice. Four known xanthones namely Decussatin (1), Gentiacaulein (2) and Swertianin (3) 1, 8-dihydroxy-2, 6-dimethoxyxanthone (4) and two new xanthones 8-hydroxy-1, 2, 4, 6-tetramethoxyxanthone (5) 1, 2, dihydroxy-6-methoxyxanthone-8-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl (6) were isolated. Among the isolated xanthones, compound 3 and 6 showed stronger suppression on carrageenan-induced rat paw edema (60.28%, 71.80 %) and increase in hot plate reaction time (9.88, 11.78 sec), while reduced the number of writhing (70.60, 76.85 %) in acetic acid test.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on the results of the present study, it is concluded that compound 3 and 6 had potential anti-inflammatory and antinoceceptive which could be used as drug candidates against inflammation related conditions.
|
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)