| In vitro: |
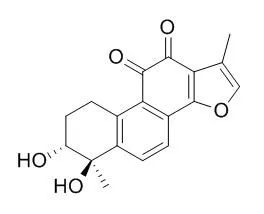
| Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, 2017, 1864(3):882-890. | | Tanshindiol C inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced macrophage foam cell formation via peroxiredoxin 1 dependent pathway.[Reference: WebLink] | NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) has been shown to be protective in atherosclerosis. The loss of Nrf2 in macrophages enhances foam cell formation and promotes early atherogenesis. Tanshindiol C (Tan C) is isolated from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge., a traditional Chinese medicine that has been used for the treatment of several cardiovascular diseases for many years. This study was aimed to test the potential role of Tan C against macrophage foam cell formation and to explore the underlying mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Firstly, we observed that Tan C markedly suppressed oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) induced macrophage foam cell formation. Then, we found that Tan C was an activator of both Nrf2 and Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) in macrophages. Nrf2 and Sirt1 synergistically activated the transcription of anti-oxidant peroxiredoxin 1 (Prdx1) after Tan C treatment. More important, we demonstrated that silencing of Prdx1 promoted oxLDL-induced macrophage foam cell formation. Prdx1 upregulated adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette (ABC) transporter A1 (ABCA1) expression and decreased intracellular lipid accumulation. Furthermore, Tan C ameliorated oxLDL induced macrophage foam cell formation in a Prdx1-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These observations suggest that Tan C protects macrophages from oxLDL induced foam cell formation via activation of Prdx1/ABCA1 signaling and that Prdx1 may be a novel target for therapeutic intervention of atherosclerosis. | | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2014, 24(11):2486-2492. | | Biological evaluation of tanshindiols as EZH2 histone methyltransferase inhibitors.[Reference: WebLink] | EZH2 is the core subunit of Polycomb repressive complex 2 catalyzing the methylation of histone H3 lysine-27 and closely involved in tumorigenesis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To discover small molecule inhibitors for EZH2 methyltransferase activity, we performed an inhibitor screen with catalytically active EZH2 protein complex and identified tanshindiols as EZH2 inhibitors. Tanshindiol B and Tanshindiol C potently inhibited the methyltransferase activity in in vitro enzymatic assay with IC50 values of 0.52 μM and 0.55 μM, respectively. Tanshindiol C exhibited growth inhibition of several cancer cells including Pfeiffer cell line, a diffuse large B cell lymphoma harboring EZH2 A677G activating mutation. Tanshindiol treatment in Pfeiffer cells significantly decreased the tri-methylated form of histone H3 lysine-27, a substrate of EZH2, as revealed by Western blot analysis and histone methylation ELISA. Based on enzyme kinetics and docking studies, we propose that tanshindiol-mediated inhibition of EZH2 activity is competitive for the substrate S-adenosylmethionine.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our findings strongly suggest that tanshindiols possess a unique anti-cancer activity whose mechanism involves the inhibition of EZH2 activity and would provide chemically valuable information for designing a new class of potent EZH2 inhibitors. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)