| In vitro: |
| J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2015 Jun 29:1-5. | | Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors isolated from Artemisia roxburghiana.[Pubmed: 26118418] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Molecular docking simulations were performed to investigate the mechanism behind PTP1B inhibition of the isolated compound and positive control, ursolic acid. Betulinic acid, betulin and Taraxeryl acetate were the active PTP1B principles with IC50 values 3.49 ± 0.02, 4.17 ± 0.03 and 87.52 ± 0.03 µM, respectively. Molecular docking studies showed significant molecular interactions of the triterpene inhibitors with Gly220, Cys215, Gly218 and Asp48 inside the active site of PTP1B. The antidiabetic activity of A. roxburghiana could be attributed due to PTP1B inhibition by its triterpene constituents, betulin, betulinic acid and Taraxeryl acetate.
CONCLUSIONS:
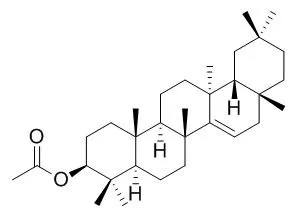
Computational insights of this study revealed that the C-3 and C-17 positions of the compounds needs extensive optimization for the development of new lead compounds. | | J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jul 30;124(3):556-61. | | Antimicrobial activity of the crude extract, fractions and compounds from stem bark of Ficus ovata (Moraceae).[Pubmed: 19450673] | This study was designed to investigate the antimicrobial activities of the methanol extracts from the stem bark of Ficus ovata (FOB), fractions (FOB1-6) and compounds isolated following bio-guided fractionation [3-friedelanone (1), Taraxeryl acetate (2), betulinic acid (3), oleanoïc acid (4), 2-hydroxyisoprunetin (5), 6,7-(2-isopropenyl furo)-5,2,4-trihydroxyisoflavone (6), Cajanin (7) and protocatechuic acid (8)].
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The micro-dilution method was used for the determination of the minimal inhibition concentration (MIC) and the minimal microbicidal concentration (MMC) against fungi (two species), gram-positive (three species) and gram-negative bacteria (five species).The results of the MIC determinations indicated that the crude extract (FOB), fractions FOB2 and FOB4 as well as compound 5 were active on the entire studied organisms. Other samples showed selective activity, fractions FOB1, FOB3 and FOB5 being active against 50% of the tested microbial species while FOB6 was active on 40%. Compounds 8, 6, 2 and 7 prevented the growth of 80%, 70%, 50% and 20% of the organisms respectively. The lowest MIC value (156 g/ml) observed with the crude extract was recorded on Streptococcus faecalis, Candida albicans and Microsporum audouinii. The corresponding value for fractions (39 microg/ml) was noted with FOB4 against Staphylococcus aureus, while that of the tested compounds (10 microg/ml) was observed with compound 8 on Microsporum audouinii.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of the MMC determination suggested that the cidal effect of most of the tested samples on the studied microorganisms could be expected. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)