| Kinase Assay: |
| Am J Transl Res. 2016 Dec 15;8(12):5455-5464. | | Trichosanatine alleviates oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced endothelial cells injury via inhibiting the LOX-1/p38 MAPK pathway.[Pubmed: 28078016 ] | The LOX-1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway has been proved to participate in the endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Trichosanatineis is an active compound isolated from the peel of Trichosanthes kirilowii. This study aims to determine whether Trichosanatine prevents the oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced insult through inhibition of the LOX-1/p38 MAPK pathway in HUVECs.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
HUVECs were treated with 150 mg/ml ox-LDL for 24 h to establish an ox-LDL-induced endothelial injury model. Cell viability, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), apoptosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, LOX-1 and p38 MAPK expression level were measured. The results indicated that HUVECs were pretreated with either 100 mM Trichosanatine or LOX-1 shRNA prior to exposure to ox-LDL for 24 h. Exposure of HUVECs to 150 mg/ml ox-LDL for 24 h significantly up-regulated the expression levels of LOX-1. The increased expression levels of LOX-1 were markedly attenuated by pretreatment with 100 mM Trichosanatine. In addition, the ox-LDL-induced increase in phosphorylated (p) p38 MAPK expression was ameliorated by pretreatment with LOX-1 shRNA. Pretreatment of HUVECs with either Trichosanatine or LOX-1 shRNA before exposure to ox-LDL significantly inhibited the ox-LDL-induced injuries, as evidenced by an increase in cell viability, a decrease in apoptotic cells, a ROS generation and a loss of MMP.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, we have demonstrated for the first time that the LOX-1/p38 MAPK pathway contributes to the ox-LDL-induced injury in HUVECs. Meanwhile, the Trichosanatine protects the HUVECs against ox-LDL-induced injury at least in part by inhibiting the activated of LOX-1/p38 MAPK pathway. |
|
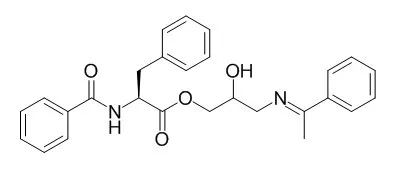
| Structure Identification: |
| Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:436863. | | Potential Protein Phosphatase 2A Agents from Traditional Chinese Medicine against Cancer.[Pubmed: 24868239] | Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is an important phosphatase which regulates various cellular processes, such as protein synthesis, cell growth, cellular signaling, apoptosis, metabolism, and stress responses. It is a holoenzyme composed of the structural A and catalytic C subunits and a regulatory B subunit. As an environmental toxin, okadaic acid, is a tumor promoter and binds to PP2A catalytic C subunit and the cancer-associated mutations in PP2A structural A subunit in human tumor tissue; PP2A may have tumor-suppressing function. It is a potential drug target in the treatment of cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we screen the TCM compounds in TCM Database@Taiwan to investigate the potent lead compounds as PP2A agent. The results of docking simulation are optimized under dynamic conditions by MD simulations after virtual screening to validate the stability of H-bonds between PP2A- α protein and each ligand. The top TCM candidates, Trichosanatine and squamosamide, have potential binding affinities and interactions with key residues Arg89 and Arg214 in the docking simulation. In addition, these interactions were stable under dynamic conditions.
CONCLUSIONS:
Hence, we propose the TCM compounds, Trichosanatine and squamosamide, as potential candidates as lead compounds for further study in drug development process with the PP2A- α protein. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)