| Structure Identification: |
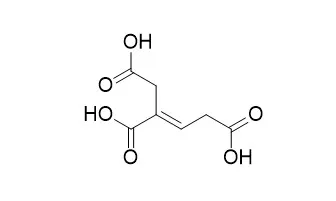
| Phytochemistry Volume 9, Issue 4, April 1970, Pages 845-851 | | Isolation and structure determination of triglochinin, a new cyanogenic glucoside from Triglochin maritimum[Reference: WebLink] | | A new cyanogenic glucoside, triglochinin (O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl]-1-cyano-1-hydroxy-4,5-dicarboxy-1,3-pentadiene), was isolated from the flowers of Triglochin maritimum L. On hydrolysis, the glucoside decomposes (inter alia) to a new acid, Triglochinic acid (2-butene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid). The isolation and structure determination of the glucoside are described. | | Acta Chem Scand . 1970;24(8):3075-8. | | Stereoselective synthesis of triglochinic acid, (E)-2-butene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid, derived from the cyanogenic glucoside triglochinin[Pubmed: 5507491] | | | RSC Adv . 2019 Apr 16;9(21):11774-11780. | | Study on the identification of Pinelliae rhizoma and Pinelliae pedatisectae rhizoma based on the characteristic component triglochinic acid[Pubmed: 35516978] | | For the first time, a monomeric compound, Triglochinic acid, has been isolated from the tubers of Pinellia pedatisecta Schott with its structure analyzed using NMR. Its molecular formula is C7H8O6, with the chemical name (2E)-but-2-ene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid. Through HPLC-DAD and HPLC-MS analysis studies, it has concluded that Pinelliae rhizoma does not contain Triglochinic acid, while Pinelliae pedatisectae rhizoma does. This key observation was used as a characteristic component to distinguish these two herbs. We analyzed 39 batches of Pinelliae rhizoma collected in herbal medicine market, among which Triglochinic acid was detected in 27 batches, resulting in a adulteration ratio of Pinelliae rhizoma reaching 69.2%. Our method demonstrates great potential for authenticating the products, thus ensuring the quality of Pinelliae rhizoma. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)