| In vitro: |
| J Agric Food Chem. 2013 May 15;61(19):4546-50. | | Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial evaluation of neovestitol and vestitol isolated from Brazilian red propolis.[Pubmed: 23607483 ] | The objective of this study was to evaluate anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities of neovestitol and vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) isolated from Brazilian red propolis (BRP).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
BRP ethanolic extract (EEP), neovestitol, and vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) were evaluated by anti-inflammatory properties using a neutrophil migration assay. The antimicrobial activity was evaluated by minimal inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations (MIC and MBC) against Streptococcus mutans , Streptococcus sobrinus , Staphylococcus aureus , and Actinomyces naeslundii . Neovestitol, vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol), and EEP inhibited neutrophil migration at a dose of 10 mg/kg. Regarding antimicrobial activity, neovestitol showed MICs ranging from <6.25 to 25-50 μg/mL and MBCs ranging from 25-50 to 50-100 μg/mL, while vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) showed MICs ranging from 25-50 to 50-100 μg/mL and MBCs ranging from 25-50 to 50-100 μg/mL.
CONCLUSIONS:
Both isoflavonoids neovestitol and vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) are consistent bioactive compounds displaying anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities that can strongly act in a low dose and concentration and have a promising potential to be applied in the pharmaceutical and food industries. | | Fine Chemicals, 2004, 21(7):525-8. | | Antioxidation Activities of Natural Components from Dalbergia odorifera T.Chen[Reference: WebLink] | The antioxidation activities of natural components extracted from Dalbergia odorifera T.Chen on lard and ascidian oil were investigated by OSI.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
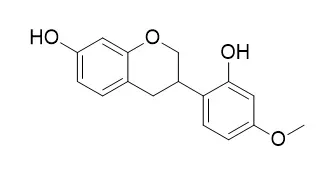
Dalbergia odorifera T.Chen was extracted with 95% ethanol,and the extract was then extracted by petroleum ether,CHCl_3,EtOAc and BuOH successively.The residue of EtOAc had very good antioxidation activity.Eight components were isolated from it,i.e.,2,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzophenone(Ⅰ),2′,3′,7-trihydroxy-4-methoxyisoflavone(Ⅱ),3′-methoxydaidzin(Ⅲ),4′,5,7-trihydroxy-3-methoxyflavone(Ⅳ),vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol,Ⅴ),medicarpin(Ⅵ),2-propenyl hexanoate(Ⅶ) and ethyl hexadecanoate(Ⅷ).
CONCLUSIONS:
The results showed that components Ⅰ,Ⅲ,Ⅴ and Ⅵ had antioxidation activity and components Ⅱ and Ⅳ had strong antioxidant activities both on lard and ascidian oil at 0.02% and 0.04% levels. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Nat Prod. 2016 Apr 22;79(4):954-60. | | Vestitol Isolated from Brazilian Red Propolis Inhibits Neutrophils Migration in the Inflammatory Process: Elucidation of the Mechanism of Action.[Pubmed: 26938776 ] | Vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) is an isoflavonoid isolated from Brazilian red propolis with potential anti-inflammatory activity. This study investigated the mechanism of action of vestitol on the modulation of neutrophil migration in the inflammatory process.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Pre-treatment with vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) at 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg reduced LPS- or mBSA-induced neutrophil migration and the release of CXCL1/KC and CXCL2/MIP-2 in vivo. Likewise, pre-treatment with vestitol at 1, 3, or 10 μM reduced the levels of CXCL1/KC and CXCL2/MIP-2 in macrophage supernatants in vitro. Moreover, the administration of vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) (10 mg/kg) reduced leukocyte rolling and adherence in the mesenteric microcirculation of mice. The pre-treatment with vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) (10 mg/kg) in iNOS(-/-) mice did not block its activity concerning neutrophil migration. With regard to the activity of vestitol on neutrophils isolated from the bone marrow of mice, there was a reduction on the chemotaxis of CXCL2/MIP-2 or LTB4-induced neutrophils and on calcium influx after pre-treatment with the compound at 3 or 10 μM. There was no change in CXCR2 expression by neutrophils treated with vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) at 10 μM.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings demonstrate that vestitol((+/-)-Vestitol) is a promising novel anti-inflammatory agent. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)