| In vitro: |
| Dar N J , Bhat J A Molecular Neurobiology, 2017, 54(7):5061-5073. | | Withanone, an Active Constituent from Withania somnifera, Affords Protection Against NMDA-Induced Excitotoxicity in Neuron-Like Cells.[Reference: WebLink] | Withania somnifera has immense pharmacologic and clinical uses. Owing to its similar pharmacologic activity as that of Korean Ginseng tea, it is popularly called as Indian ginseng. In most cases, extracts of this plant have been evaluated against various diseases or models of disease. However, little efforts have been made to evaluate individual constituents of this plant for neurodegenerative disorders.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Present study was carried out to evaluate Withanone, one of the active constituents of Withania somnifera against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in retinoic acid, differentiated Neuro2a cells. Cells were pre-treated with 5, 10 and 20 μM doses of Withanone and then exposed to 3-mM NMDA for 1 h. MK801, a specific NMDA receptor antagonist, was used as positive control. The results indicated that NMDA induces significant death of cells by accumulation of intracellular Ca2+, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, crashing of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, release of cytochrome c, increased caspase expression, induction of lipid peroxidation as measured by malondialdehyde levels and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (Parp-1), which is indicative of DNA damage. All these parameters were attenuated with various doses of Withanone pre-treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Withanone may serve as potential neuroprotective agent. | | Journal of Biotechnology, 2013, 168(2):229-233. | | Withanone as an inhibitor of survivin: A potential drug candidate for cancer therapy.[Reference: WebLink] |
Survivin, the smallest inhibitor of apoptosis protein, which has been reported to be highly expressed in almost all known cancers, plays a dual role in survival as well as the proliferation of cancer cells.
It inhibits apoptosis by inhibiting caspases as well as facilitating mitosis by becoming a part of chromosomal passenger complex through its BIR5 domain.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Docking studies carried out with herbal ligand Withanone derived from roots of Withania somnifera have shown strong binding affinity of −19.1088 kJ/mol with BIR5 domain of survivin and in turn interferes with inhibitory action against caspases and may lead to apoptosis. Binding of Withanone at BIR5 domain of survivin may also interfere with chromosomal passenger complex and lead to halt the mitotic process within the cancer cell.
CONCLUSIONS:
Docking studies support various experimental outcomes and suggest Withanone as a potential candidate molecule in cancer therapy. |
|


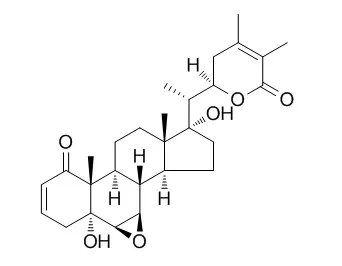



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)