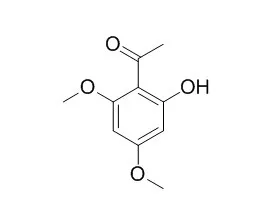
| Description: |
Xanthoxyline has antispasmodic, fungistatic, antinociceptive and antioedematogenic activities. Xanthoxylin has inhibitory effect on blood platelet aggregation; it induces melanogenesis mainly via cAMP-mediated PKA activation, other signaling pathways may also play a role in xanthoxylin-induced melanogenesis. |
| Targets: |
PKA | cAMP | PKC | Antifection |
| In vitro: |
| Asian Biomed., 2012, 6(3):413-22. | | Effect of xanthoxylin on melanin content and melanogenic protein expression in B16F10 melanoma[Reference: WebLink] | Reduced production of melanin and decreased or absence of melanocytes leads to various hypopigmentation disorders. Melanin synthesis is regulated by melanogenic proteins such as tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP-1) and tyrosinase-related protein 2 (TRP -2), as well as their transcription factors. This study elucidated the effects of Xanthoxylin on melanin content, dendriticity, melanogenic protein expression and its signal transduction pathways in mouse B16F10 melanoma cells (B16F10 cells).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Melanin production of B16F10 cells was measured by using a melanin content assay. The effect of Xanthoxylin on the dendriticity of B16F10 cells was determined by a melanocyte dendricity assay. RT-PCR was used to investigate the effects of Xanthoxylin on the melanogenic protein expression. We found that Xanthoxylin increased melanin production, number of dendrites, tyrosinase, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) expression in cultured B16F10 cells. In addition, PKA and PKC inhibitor decreased melanin production, tyrosinase, and MITF expression in Xanthoxylin-treated cells. However, Xanthoxylin did not inhibit TRP-1 and TRP-2 expression.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicated that Xanthoxylin induces melanogenesis mainly via cAMP-mediated PKA activation. Other signaling pathways may also play a role in Xanthoxylin-induced melanogenesis. | | J Pharm Sci. 1995 Apr;84(4):473-5. | | Antispasmodic activity of xanthoxyline derivatives: structure-activity relationships.[Pubmed: 7629739] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antispasmodic activity of several Xanthoxyline derivatives against acetylcholine-induced contraction of the guinea pig ileum was evaluated in vitro. The acetophenones with two methoxyl groups, mainly in the 3,4 positions, exhibited potent antispasmodic activity. Modification of the hydroxyl group in Xanthoxyline by the introduction of benzoyl, acetyl, or tosyl groups produced inactive compounds, whereas the introduction of benzyl or p-methoxybenzyl groups furnished compounds that were four- to eight-fold more potent than Xanthoxyline. In marked contrast, the introduction of a methyl group gave a compound that caused contractant activity. Modification of the carbonyl group of Xanthoxyline lead to inactive compounds, whereas the condensation of Xanthoxyline with benzaldehydes gave chalkones that were about fivefold more potent than Xanthoxyline. The introduction of benzyl and styrene groups, on the basis of the similarity with papaverine, improves the antispasmodic action of the Xanthoxyline derivates.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that the methoxyl and carbonyl groups are critical structural points for the antispasmodic activity of Xanthoxyline derivatives. The hydroxyl group improves antispasmodic activity, but is not fundamental to its manifestation. | | Arzneimittelforschung. 1999 Dec;49(12):1039-43. | | In vitro antifungal evaluation and studies on the mode of action of xanthoxyline derivatives.[Pubmed: 10635452] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study describes the fungistatic effect of Xanthoxyline (CAS 90-24-4) and its derivatives against a panel of yeasts, filamentous fungi and dermatophytes, by using the agar dilution method. Results indicated that simple structural modifications led to more potent derivatives, especially in relation with dermatophytes. The most active compound tested (10), which is a benzenesulphonyl derivative, was 12-fold more potent than Xanthoxyline itself against Trichophyton rubrum.
CONCLUSIONS:
The evaluation of the mode of action with the whole cell Neurospora crassa assay, suggested that some selected compounds may be acting by the inhibition of fungal cell-wall polymers synthesis or assembly. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Traditional Chinese Drug Research & Clinical Pharmacology,2000, 11(6):352-3. | | Inhibitory Effect of Xanthoxylin on Blood Platelet Aggregation in Rabbits.[Reference: WebLink] | Turbidimetry was used to examine the inhibitory effect of Xanthoxyin on adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-, arachidic acid (AA )- and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation in rabbits.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In-vitro experiment showed that Xanthoxyin 0.037,0.l85,0.924,9.240,92.40μmol. L -1 , can significantly inhibit ADP-, AA- and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. The inhibition rates were 22.4%-70.l%,l5.3%-68.2% and 25.8%-74.6% respectively. In-vivo experiment showed that Xanthoxylin (ig. 5 mg/kg) cand also inhibited ADP-, AA-and throbin-induced platelet aggregations. The inhibition rates were 2l.0%,35.7%,50.9% and 32.7% in ADP-induced group,23.2%,46.3%,52.4% and 4l.6% in AA-induced group, and 26.7%, 44.5%,6l.6% and 54.2% in thrombin-induced group respectively l5,30, 60 and 90 minutes after ig. Xanthoxylin. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)