| Description: |
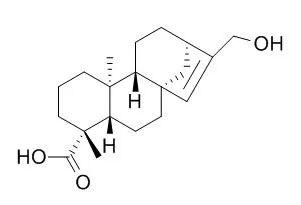
ent-17-Hydroxykaur-15-en-19-oic acid shows cytotoxicity against human prostate (22Rv1, LNCaP), colon (HT29, HCT116, SW480, SW620), and breast (MCF-7) tumor cells at concentrations ranging from 6 to 50microg/mL. |
| In vitro: |
| Cancer Lett. 2006 Dec 8;244(2):190-4. | | Kaurene diterpenes from Laetia thamnia inhibit the growth of human cancer cells in vitro.[Pubmed: 16448743 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four ent-kaurene diterpenes were isolated from the leaves of Laetia thamnia L.: ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid (1a), ent-3beta-hydroxykaur-16-ene (2), ent-kaur-16-en-3alpha,19-diol (3a), and ent-17-Hydroxykaur-15-en-19-oic acid (4). The methyl ester (1b) of compound 1a and the acetate diester (3b) of compound 3a were prepared, and all compounds were evaluated for cytotoxicity against human prostate (22Rv1, LNCaP), colon (HT29, HCT116, SW480, SW620), and breast (MCF-7) tumor cells at concentrations ranging from 6 to 50microg/mL.
CONCLUSIONS:
The kaurenes showed activity in all cell lines tested, with the prostate cells demonstrating the most sensitivity as follows: 22 Rv1 cells towards 1a (IC(50) 5.03microg/mL) and 1b (IC(50) 6.81microg/mL), and LNCaP towards 2 (IC(50) 12.83microg/mL) and 4 (IC(50) 17.63microg/mL). | | Ultrason Sonochem. 2014 Jul;21(4):1578-84. | | Bio-guided optimization of the ultrasound-assisted extraction of compounds from Annona glabra L. leaves using the etiolated wheat coleoptile bioassay.[Pubmed: 24556321 ] | A bio-guided optimization of the extraction of bioactive components from Annona glabra leaves has been developed using the etiolated wheat coleoptile bioassay as the control method.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The optimization of an ultrasound-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds using allelopathy results as target values has been carried out for the first time. A two-level fractional factorial experimental design was applied to optimize the ultrasound-assisted extraction. The solvent was the extraction variable that had the most marked effect on the resulting bioactivity of the extracts in the etiolated wheat coleoptile bioassay. Extraction time, extraction temperature and the size of the ultrasonic probe also influenced the bioactivity of the extracts. A larger scale extraction was carried out in the next step in the allelopathic study, i.e., the isolation of compounds from the bioactive extract and chemical characterization by spectroscopic techniques, including NMR. Eight compounds were isolated and identified from the active extracts, namely two steroids (β-sistosterol and stigmasterol), five diterpenes with the kaurane skeleton (ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid, ent-19-methoxy-19-oxokauran-17-oic acid, annoglabasin B, ent-17-Hydroxykaur-15-en-19-oic acid and ent-15β,16β-epoxy-17-hydroxy-kauran-19-oic acid) and the acetogenin asimicin.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most active compound was annoglabasin B, which showed inhibition with values of -95% at 10(-3) M, -87% at 5×10(-4) M and greater than -70% at 10(-4) M in the etiolated wheat coleoptile bioassay. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)