| In vitro: |
| PLoS One. 2015 Jun 11;10(6):e0128365. | | Brown Pine Leaf Extract and Its Active Component Trans-Communic Acid Inhibit UVB-Induced MMP-1 Expression by Targeting PI3K.[Pubmed: 26066652] |
Japanese red pine (Pinus densiflora) is widely present in China, Japan, and Korea. Its green pine leaves have traditionally been used as a food as well as a coloring agent. After being shed, pine leaves change their color from green to brown within two years, and although the brown pine leaves are abundantly available, their value has not been closely assessed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the potential anti-photoaging properties of brown pine leaves for skin. Brown pine leaf extract (BPLE) inhibited UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) expression to a greater extent than pine leaf extract (PLE) in human keratinocytes and a human skin equivalent model. HPLC analysis revealed that the quantity of trans-Communic acid (TCA) and dehydroabietic acid (DAA) significantly increases when the pine leaf color changes from green to brown. BPLE and TCA elicited reductions in UVB-induced MMP-1 mRNA expression and activator protein-1 (AP-1) transactivation by reducing DNA binding activity of phospho-c-Jun, c-fos and Fra-1. BPLE and TCA also inhibited UVB-induced Akt phosphorylation, but not mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), known regulators of AP-1 transactivation. We additionally found that BPLE and TCA inhibited phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), the upstream kinase of Akt, in vitro. In summary, both BPLE and its active component TCA exhibit protective effects against UVB-induced skin aging.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these findings underline the potential for BPLE and TCA to be utilized as anti-wrinkling agents and cosmetic ingredients, as they suppress UVB-induced MMP-1 expression. | | J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Dec 10;126(3):500-5. | | Antimycobacterial terpenoids from Juniperus communis L. (Cuppressaceae).[Pubmed: 19755141] | The antimycobacterial activity of Juniperus communis was attributed to a sesquiterpene identified as longifolene (1) and two diterpenes, characterised as totarol (2) and trans-Communic acid (3).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
All compounds were identified following analysis of their spectroscopic data (1D- and 2D-NMR, MS) and by comparison with the literature and commercial authentic standards when available. Revised assignments for 3 are reported. Totarol showed the best activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H(37)Rv (MIC of 73.7 microM). It was also most active against the isoniazid-, streptomycin-, and moxifloxacin-resistant variants (MIC of 38.4, 83.4 and 60 microM, respectively). Longifolene and totarol were most active against the rifampicin-resistant variant (MICs of 24 and 20.2 microM, respectively). Totarol showed the best activity in the LORA assay (MIC of 81.3 microM) and against all NTM species (MICs in the range of 7-14 microM). trans-Communic acid showed good activity against Mycobacterium aurum (MIC of 13.2 microM). The low selectivity indices (SI) obtained following cytotoxicity studies indicated that the isolated terpenoids were relatively toxic towards mammalian cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of the isolation of (1) and (2) from Juniperus communis roots, and of (3) from the aerial parts.
The antimycobacterial activity of (1) and (3), and the activity of (2) against Mycobacterium aurum, Mycobacterium fortuitum and Mycobacterium phlei, is reported for the first time. The effect of totarol on drug-resistant variants and non-replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis has never been published. |
|


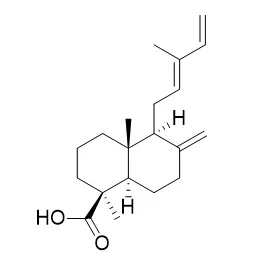



 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)