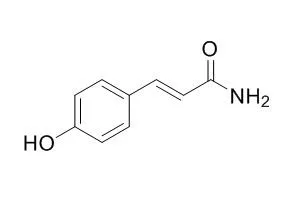
| In vitro: |
| Cancer Res. 1989 May 1;49(9):2374-8. | | Specific inhibitors of tyrosine-specific protein kinases: properties of 4-hydroxycinnamamide derivatives in vitro.[Pubmed: 2706625] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Inhibition by seven synthetic 4-Hydroxycinnamamide derivatives, ST 271, ST 280, ST 458, ST 494, ST 633, ST 638, and ST 642, of tyrosine-specific protein kinases (tyrosine kinase) of oncogene or proto-oncogene products (p130gag-v-fps, p70gag-actin-v-fgr, pp60v-src, pp60c-src) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor kinase were investigated. ST 638 (alpha-cyano-3-ethoxy-4-hydroxy-5-phenylthiomethylcinnamamide) strongly inhibited more of the tyrosine kinases than any of the other compounds. The susceptibilities of these tyrosine kinases to ST 638 increased in the following order: EGF receptor greater than p70gag-actin-v-fgr greater than pp60c-src greater than p130gag-v-fps, pp60v-src, with 50% inhibitory concentration values of 1.1, 4.2, 18, 70, and 87 microM, respectively. The phosphorylation of the tyrosine residues in particulate fractions from RR1022 cells expressing pp60v-src was inhibited by ST 638 in a dose-dependent way, while it had a negligible effect on the phosphorylations of threonine and serine residues. Kinetic analysis showed that ST 638 competitively inhibited the phosphorylation of an exogenous substrate by the EGF receptor kinase with a Ki of 2.1 microM. ST 638 noncompetitively inhibited autophosphorylation by EGF receptor kinase.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that ST 638 is a potent and specific inhibitor of tyrosine kinases in vitro, and that its inhibitory activity is caused by competing with the substrate protein for the tyrosine kinase binding site. | | Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 7;89:628-37. | | Development of 3-hydroxycinnamamide-based HDAC inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity.[Pubmed: 25462271] | Inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs) has diverse effects on cell function, such as causing differentiation, growth arrest and apoptosis in nearly all types of tumor cell lines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In our previous work, we have designed and synthesized a novel series of 4-Hydroxycinnamamide-based and 3-hydroxycinnamamide-based HDAC inhibitors (HDACIs), among which, 3-hydroxycinnamamide-based HDACIs 1a-1c exhibited moderate inhibition against HDACs. In this article, we report the development of a more potent class of 3-hydroxycinnamamide-based HDACIs, compound 7o exhibited much higher pan-HDAC inhibitory activity than positive control SAHA. In addition, compound 7h showed excellent in vitro growth inhibitory activity against more than ten cell lines and induced U937 cells apoptosis in micromolar concentration.
CONCLUSIONS:
In vivo assay in U937 xenograft model identified compound 7h as a potent, orally active HDACI. | | Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2002 Sep 16;12(18):2599-602. | | Synthesis and evaluation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid amides and 4-hydroxycinnamamides as antioxidants.[Pubmed: 12182869] | 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid amides and 4-Hydroxycinnamamides were synthesized and their antioxidant and neuroprotective activities were evaluated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Among the prepared compounds, 8b, and exhibited potent inhibition of lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenates, and marked DPPH radical scavenging activities. Furthermore, and exhibited neuroprotective action against the oxidative damage induced by the exposure of primary cultured rat cortical cells to H(2)O(2), xanthine/xanthine oxidase, or Fe(2+)/ascorbic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on these results, we found that was the most potent antioxidant among the compounds tested. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)