| Structure Identification: |
| Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;36(24):3457-62. | | Studies on chemical constitutes from callus cultures of Stellera chamaejasme.[Pubmed: 22368856] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
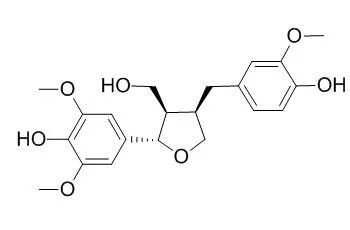
From callus cultures of Stellera chamaejasme, 17 compounds were isolated. Based on their physical and chemical data and spectroscopic analysis, they were identified as syringaresinol (1), medioresinol (2), pinoresinol (3), (1R, 2S, 5R, 6S)- 2-(4- hydroxyphenyl)-6-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-3, 7-dioxabicyclo [3, 3, 0] octane (4), epipinoresinol (5), caruilignan D (6), 3-oxo-guai-4-ene-11, 12-diol (7), (-) -lariciresinol (8), tetrahydro-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-4-[(4-hydroxyphenyl) methyl]-3-furanmethanol (9), 5'-Methoxylariciresinol (10), vladinol D (11), cyclo (L-Pro-L-Val) (12), oxomatairesinol (13), (+) -guayarol (14); acutissimalignan B (15), isolariciresinol (16), and beta-sitosterol (17), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these compounds, 12 was a cyclodipeptide, 7 was a sesquiterpene, and the others except 17 were lignans. All compounds were first isolated from callus cultures of S. chamaejasme. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 May;37(9):1241-4. | | Non-alkaloid chemical constituents from Coptis chinensis.[Pubmed: 22803368] | To separate and identify chemical constituents from Coptis chinensis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were separated and purified by various chromatographic techniques. Their structures were identified on the basis of their physicochemical properties using spectral techniques such as NMR and MS. Thirteen compounds were separated from ethanol extracts of C. chinensis, including seven lignans, three simple phenylpropanoids, two flavones and one phenolic acid, and identified as erythro-guaiacylglycerol-8-O-4'-(coniferyl alcohol) ether (1), threo-guaiacylglycerol-8-O-4'-(coniferyl alcohol) ether (2), (+)-pinoresinol (3), (+)-medioresinol (4), (+)-lariciresinol (5), (+)-5'-Methoxylariciresinol (6), (+)-isolariciresinol (7), chlorogenic acid (8), ferulic acid (9), Z-octadecyl caffeate (10), rhamnetin (11), wogonin (12), and vanillic acid (13).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1, 2, 4, 6, 10-13 were separated from the genus Coptis for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)