| In vitro: |
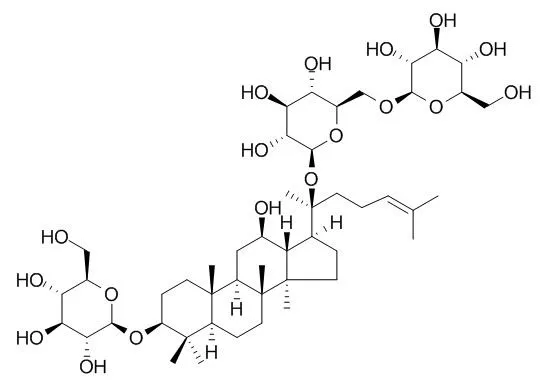
| Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Aug 15;279(1):63-75. | | Attenuation of Aβ25-35-induced parallel autophagic and apoptotic cell death by gypenoside XVII through the estrogen receptor-dependent activation of Nrf2/ARE pathways.[Pubmed: 24726523] | Amyloid-beta (Aβ) has a pivotal function in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate Aβ neurotoxicity, we used an in vitro model that involves Aβ25-35-induced cell death in the nerve growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells. Aβ25-35 (20μM) treatment for 24h caused apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by significant cell viability reduction, LDH release, phosphatidylserine externalization, mitochondrial membrane potential disruption, cytochrome c release, caspase-3 activation, PARP cleavage, and DNA fragmentation in PC12 cells. Aβ25-35 treatment led to autophagic cell death, as evidenced by augmented GFP-LC3 puncta, conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II, and increased LC3-II/LC3-I ratio. Aβ25-35 treatment induced oxidative stress, as evidenced by intracellular ROS accumulation and increased production of mitochondrial superoxide, malondialdehyde, protein carbonyl, and 8-OHdG. Phytoestrogens have been proved to be protective against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and regarded as relatively safe targets for AD drug development. Gypenoside XVII (GP-17) is a novel phytoestrogen isolated from Gynostemma pentaphyllum or Panax notoginseng. Pretreatment with Gypenoside XVII(10μM) for 12h increased estrogen response element reporter activity, activated PI3K/Akt pathways, inhibited GSK-3β, induced Nrf2 nuclear translocation, augmented antioxidant responsive element enhancer activity, upregulated heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) expression and activity, and provided protective effects against Aβ25-35-induced neurotoxicity, including oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagic cell death. In conclusion, Gypenoside XVII conferred protection against Aβ25-35-induced neurotoxicity through estrogen receptor-dependent activation of PI3K/Akt pathways, inactivation of GSK-3β and activation of Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
This finding might provide novel insights into understanding the mechanism for neuroprotective effects of phytoestrogens or gypenosides. | | J Ginseng Res. 2012 Oct;36(4):418-24. | | Enzymatic Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 and Gypenoside XVII into Ginsenosides Rd and F2 by Recombinant β-glucosidase from Flavobacterium johnsoniae.[Pubmed: 23717145] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study focused on the enzymatic biotransformation of the major ginsenoside Rb1 into Rd for the mass production of minor ginsenosides using a novel recombinant β-glucosidase from Flavobacterium johnsoniae. The gene (bglF3) consisting of 2,235 bp (744 amino acid residues) was cloned and the recombinant enzyme overexpressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) was characterized. This enzyme could transform ginsenoside Rb1 and Gypenoside XVII to the ginsenosides Rd and F2, respectively. The glutathione S-transferase (GST) fused BglF3 was purified with GST-bind agarose resin and characterized. The kinetic parameters for β-glucosidase had apparent Km values of 0.91±0.02 and 2.84±0.05 mM and Vmax values of 5.75±0.12 and 0.71±0.01 μmol·min(-1)·mg of protein(-1) against p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside and Rb1, respectively. At optimal conditions of pH 6.0 and 37℃, BglF3 could only hydrolyze the outer glucose moiety of ginsenoside Rb1 and Gypenoside XVII at the C-20 position of aglycon into ginsenosides Rd and F2, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the recombinant BglF3 could be useful for the mass production of ginsenosides Rd and F2 in the pharmaceutical or cosmetic industry. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Apr 5;52(3):1135-50. | | Gypenoside XVII Enhances Lysosome Biogenesis and Autophagy Flux and Accelerates Autophagic Clearance of Amyloid-β through TFEB Activation.[Pubmed: 27060963 ] | A strategy for activating transcription factor EB (TFEB) to restore autophagy flux may provide neuroprotection against Alzheimer's disease. Our previous study reported that Gypenoside XVII (GP-17), which is a major saponin abundant in ginseng and Panax notoginseng, ameliorated amyloid-β (Aβ)25-35-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by regulating autophagy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we aimed to determine whether GP-17 has neuroprotective effects on PC12 cells expressing the Swedish mutant of APP695 (APP695swe) and APP/PS1 mice. We also investigated the underlying mechanism. We found that GP-17 could significantly increase Atg5 expression and the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II in APP695 cells, which was associated with a reduction in p62 expression. GP-17 also elevated the number of LC3 puncta in APP695 cells transduced with pCMV-GFP-LC3. GP-17 promoted the autophagy-based elimination of AβPP, Aβ40, and Aβ42 in APP695swe cells and prevented the formation of Aβ plaques in the hippocampus and cortex of APP/PS1 mice. Furthermore, spatial learning and memory deficits were cured. Atg5 knockdown could abrogate the GP-17-mediated removal of AβPP, Aβ40, and Aβ42 in APP695swe cells. GP-17 upregulated LAMP-1, increased LysoTracker staining, and augmented LAMP-1/LC3-II co-localization. GP-17 could release TFEB from TFEB/14-3-3 complexes, which led to TFEB nuclear translocation and the induction of autophagy and lysosome biogenesis and resulted in the amelioration of autophagy flux. The knockdown of TFEB could abolish these effects of GP-17.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, these results demonstrated that GP-17 conferred protective effects to the cellular and rodent models of Alzheimer's disease by activating TFEB. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)