| In vitro: |
| Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2008, 43(9):930-933. | | Synthesis and antinociceptive activity of seselin derivatives.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
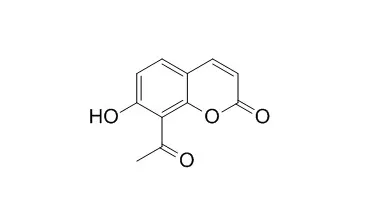
Natural product seselin and related derivatives with an angular pyranocoumarin skeleton were synthesized from 8-Acetyl-7-hydroxycoumarins by condensation with acetone,reduction,and dehydration successively under mild conditions with total yield of 50%.Twelve seselin derivatives were tested by the writhing response assay induced by acetic acid at a dose of 40 mg·kg~(-1).
CONCLUSIONS:
Seselin(4a) and 4,8,8-trimethyl-9,9-dihydro-pyranchromene-2,10-dione(2b) showed obviously antinociceptive activity with inhibitory effect of 85% and 50%,respectively,more or quite potent than aspirin in the same assay,suggesting that seselin derivatives could be a novel kind of potential antinociceptive agents. | | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2006,54(10):3521-3527. | | Antifungal and Antibacterial Activities of Mexican Tarragon (Tagetes lucida).[Reference: WebLink] | Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida Cv. Asteraceae: Campanulatae) is an important, nutritious plant and an effective herbal medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Seven coumarins, 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin (4), umbelliferone (7-hydroxycoumarin) (5), scoparone (6,7-dimethoxycoumarin) (7), esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) (11), 6-hydroxy-7-methoxycoumarin (12), herniarin (7-methoxycoumarin) (13), and scopoletin (6-methoxy-7-hydroxycoumarin) (14), and three flavonoids, patuletin (18), quercetin (19), and quercetagetin (20), were isolated from CH2Cl2 and MeOH extracts from aerial parts of T. lucida. In addition, 6,7-diacetoxy coumarin (15), 6-methoxy-7-acetylcoumarin (16), and 6-acetoxy-7-methoxycoumarin (17) derivatives were synthesized. 8-Methoxypsoralen (1), 8-Acetyl-7-hydroxycoumarin (2), 7,8-dihydroxy-6-meth-oxycoumarin (3), 6,7-dimethoxy-4-methylcoumarin (6), 5,7-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (8), 4-hydroxycoumarin (9), 4-hydroxy-6,7-dimethylcoumarin (10), naringenin (21), glycoside-7-rhamnonaringin (22), and rutin (23) were commercially obtained (Sigma-Aldrich). All of these compounds and extracts (M1 and M2) were assayed against bacteria and fungi. The antibacterial activity was determined on Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi, Salmonella sp., Shigella boydii, Shigella sp., Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter agglomerans, Sarcina lutea, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Yersinia enterolitica, Vibrio cholerae (three El Tor strains, CDC-V12, clinic case, and INDRE-206, were obtained from contaminated water), and V. cholerae (NO-O1). The evaluated fungi were Aspergillus niger, Penicillium notatum, Fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium sporotrichum, Rhizoctonia solani, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most active compounds against Gram-positive and -negative bacteria were the dihydroxylated coumarins 3 and 4. In addition, 2-4, 6, 7, and 11 showed an interesting activity against V. cholerae, a key bacterium in the contaminated water; 2-4 were the most active. Coumarins were the most effective compounds against Gram-negative bacteria. The extract MeOH/CH2Cl2 (1: 4) M2 at 0.4 microg/disk inhibited the growth of E. coli and P. mirabilis (40%), K. pneumoniae (31.1%), Salmonella sp. (35.5%), and Shigella sp. (0%) at 72 h of culture. The dimethoxy compounds 6 and 7 showed a strong activity against fungal strains, especially T. mentagrophytes and R. solani (100% of inhibition at 125.0 and 250.0 microg/mL, respectively). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)