Dried whole herbs or roots and rhizomes of Asarum campaniflorum have been sold under the trade name Xixin and used as folk remedies in its producing areas for a long time. In order to avoid the misuse of A. campaniflorum as official species of Xixin (Asari radix et rhizoma), a comparative study based on the morphological and phytochemical analysis of the aerial and underground parts was carried out.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
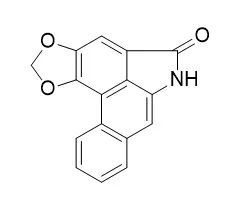
The usual morphological methods and a microscopic imaging system were used. The results show that A. campaniflorum could be easily distinguished from two official species (Asarum sieboldii and A. heterotropoides var. mandshuricum) by the diameter of thicker roots (1.3-2.7 mm), distinct large parenchymatous cells in phloem of roots, and the size of oil cells in upper leaf epidermises [(40)80-140(174) microm in diameter, where numbers in parentheses are for rare cases], etc. Nine aristolochic acid analogues (AAAs) were identified and estimated by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection (HPLC-DAD). The aerial and underground parts of A. campaniflorum contained 3-4 AAAs, i.e., aristololactam-II-N-beta-D-glucoside (AL-II-Glc), aristololactam I (AL-I), Aristololactam II (AL-II), and aristolochic acid I (AA-I), while only AL-I was detected in underground parts of A. sieboldii and no AAAs were detected in underground parts of A. heterotropoides var. mandshuricum. The respective contents (in mg/g) in aerial and underground parts of A. campaniflorum, were as follows: AL-I, 0.06-0.12, 0.05-0.10; AL-II, 0.03-0.04, 0.01-0.03; AA-I, 0.01-0.02, 0.0-0.0.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest A. campaniflorum has a high risk of causing aristolochic acid nephropathy. All these discoveries can contribute to not only the better understanding of this new resource species, but also the safe use of the crude drug Xixin. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)