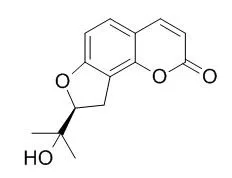
We isolated the active compound, Columbianetin. Anti-inflammatory effect of Columbianetin has been reported but the precise effects of Columbianetin in experimental models have remained unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigate the effect of Columbianetin on the production of histamine, interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) by using the human mast cell line (HMC-1). Various concentrations of Columbianetin were treated before the activation of HMC-1 cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) plus calcium ionophore, A23187. PMA plus A23187 significantly increased IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha production compared with media control (p<0.05). We also show that the increased cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha level was significantly inhibited by Columbianetin in a dose-dependent manner (p<0.05). Maximal inhibition rates of IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha production by Columbianetin were about 102.6%, 101.1%, 95.8%, and 103.9%, respectively. Columbianetin inhibited expression of COX-2. In addition, the effect of Columbianetin was investigated on the histamine release from HMC-1 stimulated by substance P, which promotes histamine release. Columbianetin also inhibited the histamine release by substance P.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, these results indicate that Columbianetin may be helpful in regulating mast cell-mediated allergic inflammatory responses. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)