| Structure Identification: |
| J Nat Med. 2009 Jan;63(1):102-4. | | Sesquiterpenes from Curcuma comosa.[Pubmed: 18663560] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
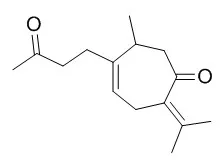
From the dried rhizomes of Curcuma comosa cultivating in Thailand, 26 known sesquiterpenes were isolated: zederone, zederone epoxide, furanodienone, isofuranodienone, 1(10)Z,4Z-furanodiene-6-one, glechomanolide, dehydrocurdione, neocurdione, curdione, 7 alpha-hydroxyneocurdione, 7 beta-hydroxycurdione, germacrone-1(10),4-diepoxide, germacrone, 13-hydroxygermacrone, curzerenone, curcolonol, alismol, alismoxide, zedoarondiol, isozedoarondiol, procurcumenol, isoprocurcumenol, aerugidiol, zedoalactone B, curcumenone, and Curcumadione. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of physicochemical evidence.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among them, glechomanolide, curzerenone, curcolonol, alismol, alismoxide, and zedoarondiol showed no significant optical activities, so they may be artifact products during the isolation or drying process. | | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008 Apr;33(7):785-8. | | Sesquiterpenes from stems and leaves of Curcuma wenyujin.[Pubmed: 18589781] | To study the chemical constituents of the stem and leaves from Curcuma wenyujin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were isolated by silica gel column chromatography in associating with Sephadex LH -20 chromatography. While their structures were identified on the basis of spectroscopic date.
Nine sesquiterpenes were isolated and identified. Their structures were identified as curdione (1), neocurdione (2), trans, trans-germacrone (3), cis, trans-germacrone (4), curcumenone (5), Curcumadione (6), isoprocurcumenol (7), glechomanolide (8) and (1R, 10R)-( -)-1, 10-dihydrocurdione (9).
CONCLUSIONS:
All of these compounds were isolated from the stems and leaves of this plant for the first time. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)