| Cell Research: |
| Biomed Pharmacother . 2019 Jan;109:1313-1318. | | Sesquiterpenes from Cyperus rotundus and 4α,5α-oxidoeudesm-11-en-3-one as a potential selective estrogen receptor modulator[Pubmed: 30551381] | | Estrogenic activity-oriented fractionation and purification of methanol extract from the rhizome of Cyperus rotundus, a well-known traditional herbal medicine, led to the isolation of six sesquiterpenes. 4α,5α-Oxidoeudesm-11-en-3-one (2) and cyper-11-ene-3,4-dione (3) together with four known sesquiterpenes, cyperotundone (1), caryophyllene α-oxide (4), α-cyperone (5), and isocyperol (6) were obtained from the hexane and dichloromethane fractions. Compounds 2 and 3 were newly isolated from natural resources in particular. To identify the possible use of isolated compounds as an alternative to hormone replacement therapy (HRT), estrogenic activity was evaluated by E-screen assay on MCF-7 BUS cells. Among the all isolated compounds from the rhizome of Cyperus rotundus, newly isolated from natural resource, 2 exhibited the most potent estrogenic activity. In an estrogen sensitive reporter gene assay, 2 significantly increased transcriptional activities. As a phytoestrogen, 2 was assessed by investigating dual action on ER-α and ER-β in competitive binding assay. It was found that 2 exerted higher binding affinity to ER-β than ER-α and it also showed both estrogenic and antiestrogenic effects depending on the E2 concentration. Our results indicate that newly isolated from Cyperus rotundus, 2 has biphasic activities on estrogen receptors which could be useful as an alternative HRT. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Molecules . 2019 Jun 14;24(12):2230. | | Anti-Migraine Effect of the Herbal Combination of Chuanxiong Rhizoma and Cyperi Rhizoma and UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of the Active Constituents in Rat Serum and Cerebral Cortex[Pubmed: 31207980] | | Chuanxiong Rhizoma and Cyperi Rhizoma (CRCR), an ancient and classic formula comprised of Chuanxiong Rhizoma and Cyperi Rhizoma in a weight ratio of 1:2, has long been used for curing migraine. This study aimed to explore their anti-migraine effect and active constituents. A nitroglycerin (NTG)-induced migraine model in rats was established to evaluate pharmacological effects. Cerebral blood flow was detected by a laser Doppler perfusion monitor. The levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), nitric oxide synthase (NOS), nitric oxide (NO), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), 5-hydoxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and β-endorphin (β-EP) were quantified with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. CGRP and c-Fos mRNA expression were quantified with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. A UPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the simultaneous quantification of active constituents in rat serum and cerebral cortex. CRCR significantly increased cerebral blood flow, decreased the levels of ET-1, GABA and NOS, and increased the levels of 5-HT, 5-HIAA and β-EP in NTG-induced migraine rats. CGRP levels and CGRP mRNA expression, as well as c-Fos mRNA expression in the brainstem were markedly down-regulated with the treatment of CRCR. After oral administration of CRCR, ferulic acid (FA), senkyunolide A (SA), 3-n-butylphthalide (NBP), Z-ligustilide (LIG), Z-3-butylidenephthalide (BDPH), cyperotundone (CYT), nookatone (NKT) and α-cyperone (CYP) were qualified in rat serum and cerebral cortex. The above results suggested that CRCR showed powerfully therapeutic effects on migraine via increasing the cerebral blood flow, decreasing the expression of CGRP and c-Fos mRNA, and regulating the releasing of ET-1, GABA, NOS, 5-HT, 5-HIAA, CGRP and β-EP in the serum and brainstem, consequently relieving neurogenic inflammation. The active constituents in CRCR for treating migraine were FA, SA, NBP, LIG, BDPH, CYT, NKT and CYP. These findings contributed for the further use of CRCR as a combinational and complementary phytomedicine for migraine treatment. | | Phytomedicine . 2020 Jan 23;70:153175. | | Zebrafish bioassay-guided isolation of antiseizure compounds from the Cameroonian medicinal plant Cyperus articulatus L[Pubmed: 32302934] | | Background: Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder affecting more than 50 million people worldwide, of whom 80% live in low- and middle-income countries. Due to the limited availability of antiseizure drugs (ASDs) in these countries, medicinal plants are the first-line treatment for most epilepsy patients. In Cameroon, a decoction of Cyperus articulatus L. rhizomes is traditionally used to treat epilepsy.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to identify and isolate the active compounds responsible for the antiseizure activity of C. articulatus in order to confirm both its traditional medicinal usage and previous in vivo studies on extracts of this plant in mouse epilepsy models.
Methods: The dried rhizomes of C. articulatus were extracted with solvents of increasing polaritie (hexane, dichloromethane, methanol and water). A traditional decoction and an essential oil were also prepared. These extracts were evaluated for antiseizure activity using a larval zebrafish seizure model with seizures induced by the GABAA antagonist pentylenetetrazole (PTZ). The hexane extract demonstrated the highest antiseizure activity and was therefore selected for bioassay-guided fractionation. The isolated bioactive compounds were characterized by classical spectroscopic methods. Since they were found to be volatile, they were quantified by GC-FID. In addition, the absorption of the active compounds through the gastrointestinal tract and the blood-brain barrier was evaluated using a hexadecane and a blood-brain barrier parallel artificial membrane permeability assays (HDM-PAMPA and PAMPA-BBB).
Results: The hexane extract of C. articulatus exhibited the highest antiseizure activity with a reduction of 93% of PTZ-induced seizures, and was therefore subjected to bioassay-guided fractionation in order to isolate the active principles. Four sesquiterpenoids were identified as cyperotundone (1), mustakone (2), 1,2-dehydro-α-cyperone (3) and sesquichamaenol (4) and exhibited significant antiseizure activity. These volatile compounds were quantified by GC in the hexane extract, the essential oil and the simulated traditional decoction. In addition, the constituents of the hexane extract including compounds 1 and 2 were found to cross the gastrointestinal barrier and the major compound 2 crossed the blood-brain barrier as well.
Conclusion: These results highlight the antiseizure activity of various sesquiterpene compounds from a hexane extract of C. articulatus dried rhizomes and support its use as a traditional treatment for epilepsy. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| J Ethnopharmacol . 2015 Aug 2;171:131-140. | | Bioactivity-guided isolation of anti-hepatitis B virus active sesquiterpenoids from the traditional Chinese medicine: Rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus[Pubmed: 26051832] | | Ethnopharmacological relevance: The rhizome of Cyperus rotundus (C. rotundus) is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine to cure hepatitis in many formulae, but the active components responsible for hepatitis have not been elucidated. According to our bioassay on HepG2.2.15 cell line in vitro, the ethanol extract of C. rotundus demonstrated potent anti-HBV activity. This current study was designed to isolate and identify the anti-HBV active constituents from the rhizomes of C. rotundus.
Material and methods: Bioactivity and LC-MS guided fractionation on the extract of C. rotundus using various chromatographic techniques including open-column, Sephadex LH-20 and semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatography led to the isolation and identification of thirty-seven sesquiterpenoids. Structural elucidation of the isolates was carried out by extensive spectroscopic analyses (UV, IR, HRMS, 1D- and 2D -NMR). The anti-HBV activity and cytotoxicity were evaluated on the HBV-transfected HepG2.2.15 cell line in vitro. The cytotoxicity effects of the isolates were assessed by a MTT assay. The secretions of HBsAg and HBeAg in the culture medium were detected by ELISA method, and the load of HBV DNA was quantified by real-time fluorescent PCR technique.
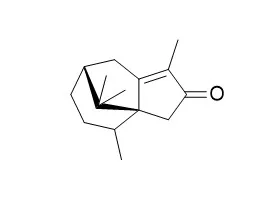
Results: Five new patchoulane-type sesquiterpenoids, namely cyperene-3, 8-dione (1), 14-hydroxy cyperotundone (2), 14-acetoxy cyperotundone (3), 3β-hydroxycyperenoic acid (4) and sugetriol-3, 9-diacetate (5), along with 32 known sesquiterpenoids were isolated from the active fractions of C. rotundus. Compounds 2 and 3 were the first cyperotundone-type sesquiterpenoids with a hydroxyl group at C-14 position. Nine eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoids (15-21 and 23-24) significantly inhibited the HBV DNA replication with IC50 values of 42.7±5.9, 22.5±1.9, 13.2±1.2, 10.1±0.7, 14.1±1.1, 15.3±2.7, 13.8±0.9, 19.7±2.1 and 11.9±0.6 μM, respectively, of which, compounds 17, 21, 23 and 24 possessed high SI values of 250.4, 125.5,>259.6 and 127.5, respectively. Two patchoulane-type sesquiterpenoids (4 and 7) effectively suppressed the secretion of HBsAg in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values of 46.6±14.3 (SI=31.0) and 77.2±13.0 (SI=1.7) μM, respectively. Compounds 2, 8, 12, 15, 17 and 25 possessed moderate activities against HBeAg secretion with IC50 values of 162.5±18.9 (SI=13.3), 399.2±90.0 (SI=10.6), 274.7±70.8 (SI=5.2), 313.9±87.5 (SI=7.2), 334.0±70.4 (SI=9.9) and 285.3±20.9 (SI=15.5) μM, respectively.
Conclusions: This is the first study to reveal the anti-HBV constituents of C. rotundus, demonstrating that the eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoids might contribute to the anti-HBV activity of the rhizomes of C. rotundus. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)