| Structure Identification: |
| Phytochemistry, 28(12):3465-3468. | | Anthraquinones and naphthohydroquinones from Rubia cordifolia.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four naphthohydroquinones and their glycosides, and 11 anthraquinones and their glycosides were isolated from the dried roots of Rubia cordifolia var. pratensis. Six of them, Dihydromollugin, 2-carbomethoxy-3-(3′- hydroxy)isopentyl-1,4-naphthohydroquinone 4-O-β-glucoside, 2-methyl-1,3,6-trihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone 3-O-β-glucoside, 2-methyl-1,3,6-trihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone 3-O-(3′-O-acetyl)-α-rhamnosyl (1→2)-β-glucoside, 2-methyl- 1,3,6-trihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone 3-O-(3′,6′-O-diacetyl)-α-rhamnosyl(1→2)-β-glucoside and 2-methyl-1,3,6-tri- hydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone 3-O-(4′,6′-O-diacetyl)-α-rhamnosyl(1→2)-β-glucoside, were isolated for the first time from a natural source.
CONCLUSIONS:
The structures were established by various chemical and spectroscopic methods. The chemotaxonomic significance of these findings is discussed briefly. | | Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2001,48(1):77-79. | | Synthesis of Naturally Occurring Rubilactone, Mollugin, and Dihydromollugin of Rubia cordifolia.[Reference: WebLink] |
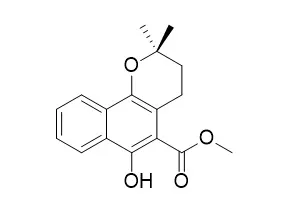
Rubilactone (1), Dihydromollugin (2), and mollugin (3) are naturally occurring products found in Rubia cordifolia, which is a famous Chinese herb with anti tumor, viral inhibition and other activities. Synthetic studies were carried out in these naphthoic acid esters starting from 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we finished the synthesis of rubilactone which has not been reported before and also synthesized Dihydromollugin and mollugin with better yields with different approaches compared to those previously reported in the literature.
|
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)