| Description: |
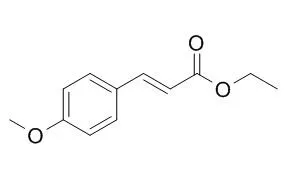
Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate(Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate) has antifungal activity, it can inhibit the growth of Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Epidermophyton floccosum at a concentration less than 10 mug/ml. Ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate has anti-inflammatory, it can dose-dependently inhibit carrageenan-induced edema with an MIC of 100 mg/kg, and non-selectively inhibit the activities of cyclooxygenases 1 and 2, with IC50 values of 1.12 uM and 0.83 uM respectively; it has chemopreventive activity against fibrosarcoma through inhibition of COX-2, and can block bFGF-induced vessel formation on Matrigel plug assay in vivo. Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate could be developed as a skin whitening agent to treat hyperpigmentary disorders. |
| In vitro: |
| Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 32(5): 2731-4. | | Cytotoxicity Activity of Biotransformed Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate by Aspergillus niger.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The extraction of Kaempferiagalanga rhizome using steam distillation and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) carried out. After fractionation, the major compound of the K. galanga, ethyl p-methoxycinnamate (EPMC) was Aspergillus ethyl p-hydroxycinnamate (Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate,EPHC). The biological activity of EPMC and its biotransformed product (EPHC) established by activity on human breast cancer (MCF-7) cell line using MTT assay. Ethyl p-hydroxycinnamate (EPHC) was most cytotoxic at 1000 μg/mL percentage cell viability was 9.87% IC50 was 340μg/mL. showed slight cytotoxicity activity compared to EPMC.
CONCLUSIONS:
that the biotransformation process was able to produce metabolite (EPHC) higher cytotoxicity activity compared to its parent compound (EPMC).
| | Phytother Res. 2014 Feb;28(2):274-9. | | Hypopigmentary effects of ethyl P-methoxycinnamate isolated from Kaempferia galanga.[Pubmed: 23610003 ] | We isolated crystals from the chloroform fraction of an ethanol extract of Kaempferia galanga and identified it as ethyl p-methoxycinnamate(Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate)through nuclear magnetic resonance analysis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we found that ethyl p-methoxycinnamate significantly decreased melanin synthesis in B16F10 murine melanoma cells stimulated with α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH). In a cell-free system, however, ethyl p-methoxycinnamate did not directly inhibit tyrosinase, the rate-limiting enzyme of melanogenesis. Instead, it inhibited tyrosinase activity in B16F10 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, Western blot analysis showed that ethyl p-methoxycinnamate decreased microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and tyrosinase levels in α-MSH-stimulated B16F10 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the pigment-inhibitory effect of ethyl p-methoxycinnamate results from downregulation of tyrosinase. Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate isolated from K. galanga could be developed as a skin whitening agent to treat hyperpigmentary disorders. | | Lloydia. 1976 Jul-Aug;39(4):218-22. | | Isolation of Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate, the major antifungal principle of Curcumba zedoaria.[Pubmed: 785141] | An antifungal principle of the dried rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria was extracted with hot ethanol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
By successive chromatography on neutral alumina and silica gel, three antibiotic compounds A, B, and C, all active against Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, were obtained in chemically pure form. By uv, ir, pmr and ms analysis, the structure of the most abundant one of these compounds (C, 69.8%; H, 6,8%; and 0.23.4%) was assigned as ethyl p-methoxycinnamate (Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate,EPMC).
The proposed structure was confirmed by synthesis and comparison of the chemical and biological properties of the natural and synthetic products.
EPMC inhibits the growth of Trichophyton rubrum, Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Epidermophyton floccosum at a concentration less than 10 mug/ml; A. fumigatus, Penicillium purpurogenum, Trignoposis variabilis, Microsporum gypseum, Sclerotium rolifsii, Geotricular candiade, Fusarium oxysporum and Helminthosporium oryzale at a concentration less than 25 mug/ml; and Candida krusei and T. mentagrophytes At a concentration less than 50 mug/ml. The spores of T. rubrum Lose viability or ability to germinate when wxposed to its ethanolic solution (30 mug/ml) for 2 hours. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Int. J. Pharm. Pharm.Sci., 2012, 4:528-32. | | Structure modification of ethyl p-methoxycinnamate and their bioassay as chemopreventive agent against mice's fibrosarcoma[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, ethyl p-methoxycinnamate(Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate) isolated from Kaempferia galanga was used as starting material to produce thiourea derivatives (4a, 4b, 4c) in a good yield. The synthesis products were confirmed by FTIR, 1 H-NMR, 13 Keywords: Kaempferia galanga, cyclooxygenase-2, Ethyl p-methoxycinnamate(Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate), Thiourea derivatives, Fibrosarcoma C-NMR and HRMS spectroscopic methods. Their activities against fibrosarcoma were tested in vivo using mouse model induced by 0.3% benzo(a)pyrene injected subcutaneously, which was given five times, once every two days.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results showed that fibrosarcoma can be inhibited by all synthesized compounds. In silico analysis predicted that one of mechanism chemopreventive activity of all synthesized compounds against fibrosarcoma through inhibition of COX-2. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)