| Structure Identification: |
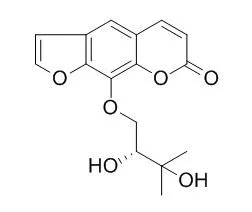
| PLoS One. 2014 Oct 14;9(10):e108713. | | Isolation, cytotoxicity evaluation and HPLC-quantification of the chemical constituents from Prangos pabularia.[Pubmed: 25314269] | Phytochemical analysis of the dichloromethane:methanol (1:1) extract of root parts of Prangos pabularia led to the isolation of twelve cytotoxic constituents, viz., 6-hydroxycoumarin (1), 7-hydroxycoumarin (2), Heraclenol-glycoside (3), xanthotoxol (4), Heraclenol (5), oxypeucedanin hydrate (6), 8-((3,3-dimethyloxiran-2-yl)methyl)-7-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (7), oxypeucedanin hydrate monoacetate (8), xanthotoxin (9), 4-((2-hydroxy-3-methylbut-3-en-1-yl)oxy)-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one (10), imperatorin (11) and osthol (12).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The isolates were identified using spectral techniques in the light of literature. 3-(4,5-dimethyl thiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) cytotoxicity screening of the isolated constituents was carried out against six human cancer cell lines including lung (A549 and NCI-H322), epidermoid carcinoma (A431), melanoma (A375), prostate (PC-3) and Colon (HCT-116) cell lines. Osthol (12) exhibited the highest cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 3.2, 6.2, 10.9, 14.5, 24.8, and 30.2 µM against epidermoid carcinoma (A431), melanoma (A375), lung (NCI-H322), lung (A549), prostate (PC-3) and colon (HCT-116) cell lines respectively. Epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431 was sensitive to most of the compounds followed by lung (A549) cancer cell line. Finally a simple and reliable HPLC method was developed (RP-HPLC-DAD) and validated for the simultaneous quantification of these cytotoxic constituents in Prangos pabularia. The extract was analyzed using a reversed-phase Agilent ZORBAX eclipse plus column C18 (4.6×250 mm, 5 µm) at 250 nm wavelength using a gradient water-methanol solvent system at a flow rate of 0.8 ml/min.
CONCLUSIONS:
The RP-HPLC method is validated in terms of recovery, linearity, accuracy and precision (intra and inter-day validation). This method, because of shorter analysis time, makes it valuable for the commercial quality control of Prangos pabularia extracts and its future pharmaceutical preparations. | | Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Oct;7(10):1327-30. | | Phytotoxic furanocoumarins from the shoots of Semenovia transiliensis.[Pubmed: 23157001] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A number of furanocoumarin compounds isolated from S. transiliensis shoots were phytotoxic to both test species. These included psoralen, isopsoralen, heratomin, isopentenyloxyisobergapten, imperatorin, bergapten, xanthotoxin, heraclenin, and Heraclenol.
CONCLUSIONS:
All the active secondary metabolites isolated from the shoots of S. transiliensis were furanocoumarins. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)