| In vitro: |
| Food Funct. 2015 Feb 11;6(2):431-43. | | Isolation and identification of ingredients inducing cancer cell death from the seeds of Alpinia galanga, a Chinese spice.[Pubmed: 25464007] | This study was carried out to isolate ingredients from the seeds of a Chinese spice (Alpinia galangal) and to evaluate their cytotoxic activity on cancer cell lines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
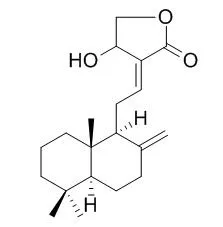
Isolation and purification of the phytochemical constituents were conducted using silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 and ODS columns. After extraction using 95% ethanol, the total extracts were re-extracted, resulting in petroleum ether (PE), ethyl acetate (EA) and water fractions, respectively. Activity tests showed that the EA fraction exhibited obvious (p < 0.05) protective effects on H2O2 damaged PC-12 cells at 20 μg mL(-1), and showed much higher (p < 0.05) cytotoxic activity on cancer cell lines than other fractions. Five compounds, 1'-S-1'-acetoxyeugenol acetate (), 1'-S-1'-acetoxychavicol acetate (), 2-propenal, 3-[4-(acetyloxy)-3-methoxyphenyl] (), Isocoronarin D () and caryolane-1, 9β-diol (), were obtained from the EA fraction and identified by HPLC, UV, MS, and NMR spectroscopic analyses. Compounds and were isolated from A. galangal for the first time. Moreover, compounds , , and were the main active ingredients for inducing death of the tested cancer cells, and their IC50 values ranged from 60 to 90 μg mL(-1), indicating that these compounds possessed a wide anti-cancer capability.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, A. galangal seeds could be a potential source of healthy food for tumor prevention. | | J Nat Prod. 2010 Apr 23;73(4):724-8. | | Labdane diterpenes from the aerial parts of Curcuma comosa enhance fetal hemoglobin production in an erythroid cell line.[Pubmed: 20196571] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new labdane diterpenes, curcucomosins A-C (1-3), four known labdane diterpenes, 4-7, and a known diarylheptanoid, 8, were isolated from the aerial parts of Curcuma comosa. The structures of the new diterpenes were elucidated by spectroscopic data analysis. The fetal hemoglobin (Hb F) induction potency of the isolated compounds was examined using a K562 reporter cell line harboring the enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) gene under the control of a (G)gamma-globin promoter.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compound 6, Isocoronarin D, exhibited the highest Hb F induction effect of 1.6-fold at 20 microM. | | Rev.Bras.Farmacogn.,2014, 24(4): 408-12. | | Cancer chemoprevention activity of labdane diterpenes from rhizomes of Hedychium coronarium[Reference: WebLink] | Hedychium coronarium J. Koenig, Zingiberaceae, is a medicinal plant popularly used to treat inflammatory conditions in different countries.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three labdane diterpenes [Isocoronarin D (1), methoxycoronarin D (2), ethoxycoronarin D (3)] and benzoyl eugenol (4) were isolated from rhizomes and their chemopreventive potential was evaluated using in vitro assays, namely the inhibition of NF-κB, COX-1 and -2, the induction of antioxidant response element (ARE), and the inhibition of cell proliferation. Diterpene 1 activated ARE (EC50 57.6 ± 2.4 μM), while 2, 3 and 4 significantly inhibited NF-κB (IC50 of 7.3 ± 0.3, 3.2 ± 0.3 and 32.5 ± 4.9 μM, respectively). In addition, 2 and 3 selectively inhibited COX-1 (IC50 values of 0.9 ± 0.0 and 3.8 ± 0.0 μM, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS:
These data support the potential chemopreventive activity of constituents from H. coronarium rhizomes. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)