| In vitro: |
| Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Apr;7(4):471-4. | | Chemical constituents of the aerial parts of Scutellaria lateriflora and their alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activities.[Pubmed: 22574444] | MeOH extracts of 37 herbs were tested in screening experiments for rat intestinal alpha-glucosidase.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
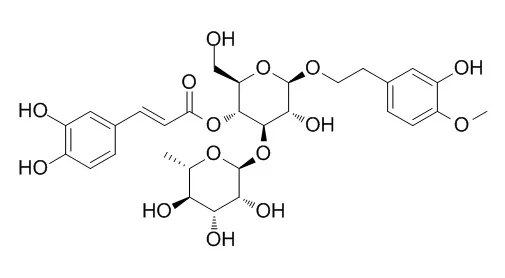
The MeOH extract of the aerial parts of Scutellaria lateriflora L. (Lamiaceae) significantly inhibited sucrase and maltase activities, using sucrose and maltase as the substrates. Enzyme inhibition guided-fractionation of the MeOH extract of S. lateriflora resulted in the isolation of a new diterpene glucoside, deacetylajugarin-IV 18-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), along with 20 known phenolics (2-21). The structures of 1-21 were elucidated on the basis of MS and NMR data analyses. Baicalein (4) and baicalin (10), a glycoside of 4, showed moderate sucrase inhibitory activities at IC50 values of 14.9 and 36.3 microM, respectively, whereas luteolin (3), acteoside (16), leucosceptoside A (18), and isoacteoside (20) showed weak inhibitory activities at IC50 values of 811, 522, 727, and 443 microM, respectively. This is the first report on mammalian alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activities of S. lateriflora extract and identification of the constituents responsible for the activities. Apigenin (2), luteolin (3), 6-methoxyluteolin 4'-methyl ether (6), isoscutellarin 8-O-beta-D-glucuronide (7), luteolin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (9), wogonin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide methyl ester (12), eriodictyol (13), naringenin (14), naringenin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (15), Jionoside D (17), leucosceptoside A (18), and (+)-syringaresinol 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (21) were isolated from this plant for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
The inhibitory properties of S. lateriflora extract against alpha-glucosidase provide a prospect for its antidiabetic usage. | | Biol Pharm Bull. 2004 Oct;27(10):1504-8. | | Antioxidant activity of jionoside D from Clerodendron trichotomum.[Pubmed: 15467185] | The antioxidant property of Jionoside D, isolated from Clerodendron trichotomum (Verbenaceae), was investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This compound showed scavenging activity of intracellular reactive oxygen species and of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical, as well as lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity. This radical scavenging activity of Jionoside D protected the cell viability of Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79-4) cells exposed H2O2. Furthermore, Jionoside D reduced the apoptotic cells induced by H2O2, as demonstrated by the decreased number of sub G1 hypo-diploid cells and apoptotic body formation. However, it increased the activities of cellular antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase and catalase.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these findings suggest that Jionoside D, isolated from C. trichotomum, exhibits antioxidant properties. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)