| Structure Identification: |
| J Asian Nat Prod Res. 1998;1(2):125-31. | | Lignans from Kadsura angustifolia.[Pubmed: 11261213] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
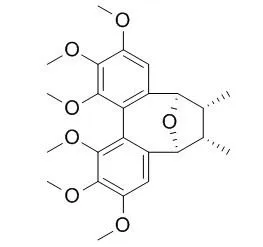
A new dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan named angustifolin D (1) together with four known lignans: kadsulignan L (2), Kadsulignan N (3), schisantherin P (4) and meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid (5) were isolated from the stems of Kadsura angustifolia. Their structures and stereochemistries were elucidated by spectral studies.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 2 and 5 showed moderate platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonistic activities with IC50 values of 2.6 x 10(-5) and 4.1 x 10(-5) M, respectively. | | J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol. 2009 Jan 1;32(16):2361-2371. | | Countercurrent Chromatographic Separation of Lipophilic Ascorbic Acid Derivatives and Extract from Kadsura Coccinea Using Hydrophobic Organic-Aqueous Two-Phase Solvent Systems.[Pubmed: 20046934] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Countercurrent chromatographic (CCC) separation of lipophilic ascorbic acid derivatives and the crude extract from Kadsura Coccinea was performed using the type-J multilayer coil planet centrifuge with a hydrophobic organic-aqueous two-phase solvent system composed of n-hexane/ethyl acetate/ethanol/aqueous 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid at the volume ratio of (5 : 5 : 6 : 2). The lipophilic ascorbic acid derivatives were separated in the order of L-ascrobyl 2,6-dibutyrate, L-ascorbyl 6-palmitate and L-ascorbyl 6-stearate by eluting the lower phase as the mobile phase, and L-ascorbyl 2,6-dipalmitate was separated by eluting the upper phase at the opposite direction. The above solvent system was then applied to the CCC separation of the extract prepared from K. coccinea. With lower phase mobile, the extract was mainly separated into two peaks corresponding to lignans and triterpenoids accordingly. The HPLC analysis of the fractions showed that the former peak contained Kadsulignan N, Schizandrin H and Neokadsuranin as lignans, and the latter peak, Micranoic acid A, Neokadsuranic acid B and beta-Sitosterol as triterpenoids.
CONCLUSIONS:
The overall results indicate that the hydrophobic organic-aqueous two-phase solvent system used in the present studies was useful for the CCC separation of lignans and triterpenoids present in the natural products. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)