| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of Chromatographic Science, 2015,53(10) 1695–1700. | | Validation of an HPLC-MS-MS Assay for Determination of Morellic Acid in Rat Plasma: Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies.[Reference: WebLink] | A selective and rapid high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–MS-MS) was developed for the quantification of Morellic acid in rat plasma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
HPLC was performed using a Capcell MG C18 (50 × 4.6 mm, i.d., 5 µm) column, and isocratic elution with water–acetonitrile (20:80, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. Sample preparation of analyte and internal standard (gambogic acid) involved liquid–liquid extraction using ethyl acetate–isopropanol (1:1, v/v) from 50 µL plasma. The precursor → production transitions for analyte and IS were m/z 559.4 → 471.3, and m/z 627.3 → 583.3, respectively, and were monitored on a triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer, operating in negative ion scan mode. The method was validated across the dynamic concentration range of 20–7,500 ng/mL for Morellic acid, with a fast run time of 6.0 min. The analytical method measured concentrations of Morellic acid with accuracy (% bias) of ≤6.4% and precision (% RSD) of ≤14.0%. Morellic acid was stable during the battery of stability studies. Finally, the applicability of this assay has been successfully demonstrated in vivo pharmacokinetic studies in Sprague–Dawley rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
This method will therefore be useful for further preclinical and clinical pharmacokinetic studies of Morellic acid. | | Journal of Natural Products, 2011, 74(3):460-463. | | Absolute configuration of (-)-gambogic acid, an antitumor agent.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
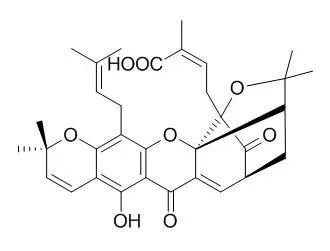
(-)-Gambogic acid (1), a biologically active "caged xanthone" from gamboge, the dried resin of Garcinia hanburyi, is of interest as a potential anticancer agent. The planar structure of (-)-gambogic acid has been determined previously by analysis of its detailed NMR data and confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, with the absolute configuration at C-13 deduced as R through a series of chemical degradations.
CONCLUSIONS:
Using (-)-Morellic acid (2), an analogue of (-)-gambogic acid, as a model compound, the 5R, 7S, 10aS, 13R, 27S absolute configuration of (-)-gambogic acid was determined for the first time by comparison of physical and spectroscopic data, especially experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)