| In vitro: |
| Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;101(11):4521-4532. | | General assay for enzymes in the heptose biosynthesis pathways using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 28280867 ] | The ADP-L-glycero-β-D-manno-heptose and the GDP-6-deoxy-α-D-manno-heptose biosynthesis pathways play important roles in constructing lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Blocking the pathways is lethal or increases antibiotic susceptibility to pathogens. Therefore, the enzymes involved in the pathways are novel antibiotic drug targets.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we designed an efficient method to assay the whole enzymes in the pathways using mass spectrometry and screened 148 compounds. One promising lead is (-)-Nyasol targeting D-glycero-α-D-manno-heptose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase (HddC) included in the GDP-6-deoxy-α-D-manno-heptose biosynthesis pathway from Burkholderia pseudomallei.
CONCLUSIONS:
The inhibitory activity of the lead compound against HddC has been confirmed by blocking the system transferring the guanosine monophosphate (GMP) moiety to α-D-glucose-1-phosphate. (-)-Nyasol exhibits the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 17.6 μM. A further study is going on using (-)-Nyasol derivatives to find better leads with high affinity.
CONCLUSIONS:
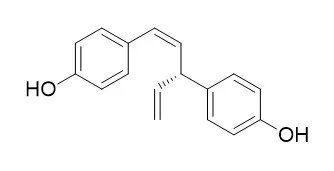
The inhibitory activity of the lead compound against HddC has been confirmed by blocking the system transferring the guanosine monophosphate (GMP) moiety to α-D-glucose-1-phosphate. (-)-Nyasol exhibits the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 17.6 μM. A further study is going on using (-)-Nyasol derivatives to find better leads with high affinity. | | Phytochemistry. 2003 Nov;64(5):997-1001. | | Isolation and anti-oomycete activity of nyasol from Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizomes.[Pubmed: 14561517] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanol extract of Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizomes exhibited strong antifungal activity against the plant pathogenic fungi Magnaphothe grisea, Rhizoctonia solani, and the plant pathogenic oomycete Phytophthora capsici. The antifungal substance isolated from the rhizomes of A. asphodeloides was identified to be Nyasol, (Z)-1,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadiene by NMR and mass spectral analysis. Nyasol effectively inhibited the mycelial growth of Colletotrichum orbiculare, P. capsici, Pythium ultimum, R. solani, and Cladosporium cucumerinum in a range of 1-50 mug/ml, but did not affect the growth of bacteria and yeast.
CONCLUSIONS:
In a greenhouse test, treatment with the antifungal compound Nyasol was significantly effective in suppressing the Phytophthora blight on pepper plants. | | J Nat Prod. 1997 Oct;60(10):1017-22. | | Antiprotozoal compounds from Asparagus africanus.[Pubmed: 9358645 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two antiprotozoal compounds have been isolated from the roots of Asparagus africanus Lam. (Liliaceae), a new sapogenin, 2 beta, 12 alpha-dihydroxy-(25R)-spirosta-4,7-dien-3-one (1), which was named muzanzagenin, and the lignan (+)-Nyasol (2), (Z)-(+)-4,4'-(3-ethenyl-1-propene-1,3-diyl)-bisphenol. The structure of the sapogenin was elucidated by MS and by 1D and 2D NMR methods and established by a single crystal X-ray analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
(+)-Nyasol potently inhibits the growth of Leishmania major promastigotes, the IC50 being 12 microM, and moderately inhibits Plasmodium falciparum schizonts with the IC50 49 microM. These concentrations only moderately affect the proliferation of human lymphocytes. Muzanzagenin showed a moderate in vitro activity in all three tests, the IC50 against leishmania promastigotes was 70 microM, and against four different malaria schizont strains the IC50 values were 16, 163, 23, and 16 microM, respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)