| In vitro: |
| Mar Drugs. 2017 May 16;15(5). | | A New Ergosterol Analog, a New Bis-Anthraquinone and Anti-Obesity Activity of Anthraquinones from the Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Talaromyces stipitatus KUFA 0207.[Pubmed: 28509846] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
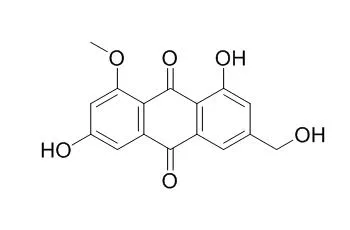
A new ergosterol analog, talarosterone (1) and a new bis-anthraquinone derivative (3) were isolated, together with ten known compounds including palmitic acid, ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one, ergosterol-5,8-endoperoxide, cyathisterone (2), emodin (4a), Questinol (4b), citreorosein (4c), fallacinol (4d), rheoemodin (4e) and secalonic acid A (5), from the ethyl acetate extract of the culture of the marine sponge-associated fungus Talaromyces stipitatus KUFA 0207. The structures of the new compounds were established based on extensive 1D and 2D spectral analysis, and in the case of talarosterone (1), the absolute configurations of its stereogenic carbons were determined by X-ray crystallographic analysis. The structure and stereochemistry of cyathisterone (2) was also confirmed by X-ray analysis. The anthraquinones 4a-e and secalonic acid A (5) were tested for their anti-obesity activity using the zebrafish Nile red assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
Only citreorosein (4c) and Questinol (4b) exhibited significant anti-obesity activity, while emodin (4a) and secalonic acid A (5) caused toxicity (death) for all exposed zebrafish larvae after 24 h. | | J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Oct;24(10):1346-53. | | Anti-inflammatory activity of questinol isolated from marine-derived fungus Eurotium amstelodami in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.[Pubmed: 24986678] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, an anthraquinone derivative, Questinol was successfully isolated from the broth extract of the marine-derived fungus Eurotium amstelodami for the first time. The structure of Questinol was determined based on the analysis of the MS and NMR spectral data as well as comparison of those data with the published data. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory effect of Questinol in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells was investigated. The results showed that Questinol did not exhibit cytotoxicity in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells up to 200 μM. Questinol could significantly inhibit NO and PGE2 production at indicated concentrations. Questinol was also found to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Furthermore, the western blot analysis showed that Questinol suppressed the expression level of iNOS in a dose-dependent manner. However, Questinol could slightly inhibit the expression of COX-2 at the concentration of 200 μM.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, our study suggests that Questinol might be selected as a promising agent for the prevention and therapy of inflammatory disease. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)