| Animal Research: |
| Biochemical pharmacology, 2009, 77(5):845-857. | | Teupolioside, a phenylpropanoid glycosides of Ajuga reptans, biotechnologically produced by IRBN22 plant cell line, exerts beneficial effects on a rodent model of colitis.[Reference: WebLink] | The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of phenylpropanoid glycoside, Teupolioside, biotechnologically produced by IRBN22 Ajuga reptans cell line, in rats subjected to experimental colitis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Colitis was induced in rats by intracolonic instillation of dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS). Teupolioside was administered daily orally (0.2 or 2mgkg(-1)). On Day 4, animals were sacrificed and tissues were taken for histological and biochemical analysis. Four days after DNBS administration, colon TNF-alpha and IL-1beta productions were increased, associated with colon damage. Neutrophil infiltration, by myeloperoxidase activity, in the mucosa was associated with up-regulation of ICAM-1 and P-selectin and high levels of malondialdehyde. Immunohistochemistry for nitrotyrosine and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) showed an intense staining in the inflamed colon. Biochemical methods and zymography were used to analyze MMP-9 and -2 activities in colon tissues from DNBS-injured rats. Treatment with Teupolioside significantly reduced the appearance of diarrhoea and the loss of body weight. This was associated with a remarkable amelioration in the disruption of the colonic architecture and a significant reduction in colonic myeloperoxidase activity and malondialdehyde levels. Teupolioside also reduced the pro-inflammatory cytokines release, the appearance of nitrotyrosine and PARP immunoreactivity in the colon and reduced the up-regulation of ICAM-1 and the expression of P-selectin. Therefore, Teupolioside also reduced proMMP-9 and -2 activity induced in the colon by DNBS administration.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of this study suggested that administration of Teupolioside may be beneficial for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. |
|
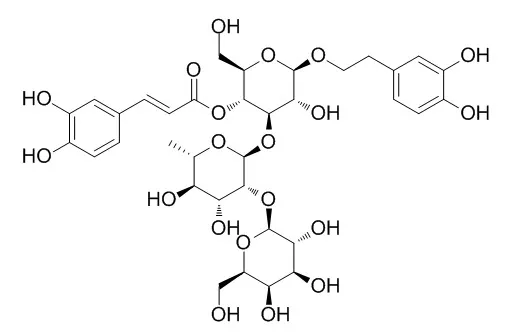
| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of Molecular Catalysis B Enzymatic, 2014, 104:42-47. | | Enzymatic acylation as an efficient tool for an easy access to specific acyl derivatives of the natural antioxidants verbascoside, teupolioside and echinacoside.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The natural antioxidants phenylpropanoids glycosides echinacoside (1), verbascoside (2) and Teupolioside (3) were efficiently and regiospecifically monoacylated by means of the enzyme lipase PS. While acylation of Teupolioside (3) and of echinacoside (1) occurred at a sugar primary OH in the “lower” or in the “upper” part of the molecule, respectively, verbascoside (2) was acetylated at one of its sugars secondary OHs.
CONCLUSIONS:
At variance to enantioselectivity, which can be rationalized in terms of steric effects due to substituents bulkiness, our new results confirm that enzyme regioselectivity is mainly dictated by the electrostatic interactions of the different OHs of the substrates with the amino acids of the enzyme. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)