| Description: |
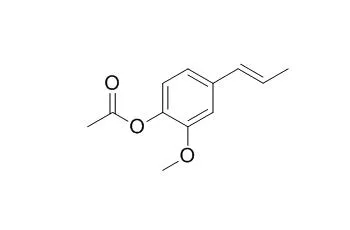
Acetylisoeugenol is a mild sensitizer in vivo, it shows good antifungal activities against R. solani and F. oxysporum. |
| Targets: |
Antifection |
| In vitro: |
| Industrial Crops & Products, 2017, 97:388-394. | | Structure-activity relationships of cinnamaldehyde and eugenol derivatives against plant pathogenic fungi.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cinnamon bark oil showed a lower activity than clove bud oil. The fungicidal activity of cinnamaldehyde (IC50 = 75.4 and 156.9 μg/mL, respectively) and eugenol (IC50 = 58.9 and 52.9 μg/mL, respectively) against R. solani and F. oxysporum was also evalutated. Comparisons of the antifungal activities of cinnamaldehyde and eugenol derivatives revealed that α-methylcinnamaldehyde, α-methylcinnamic acid, methyleugenol, acetyleugenol, isoeugenol, methylisoeugenol, and Acetylisoeugenol showed good antifungal activities against R. solani and F. oxysporum. In structure-activity relationships, the fungicidal activity of cinnamaldehyde derivatives could be related to conjugated double bond and the length of CH chain outside the ring. In addition, the presence of the lipophilicity may have a considerable influence on the toxicity of phenylpropenes.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present approach may help future work in the search for fungicidal compounds. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Dermatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):153-60. | | Factors influencing conjugation of phenolic compounds with the epsilon-amino group.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Factors influencing the conjugation potency of eugenol (E), isoeugenol (IE), methyl isoeugenol (MIE), and Acetylisoeugenol (AIE) with [l-14C]07-aminocaproic acid are investigated. The conjugation reaction for IE is accelerated in the presence of H2O2-peroxidase and inhibited under anaerobic conditions by nitrogen gas flow. An oxidation reaction is found to be necessary for the conjugation of IE with 07-aminocaproic acid. Immediately after mixing the phenolic compounds with [1-14C]07-aminocaproic acid and H2O2-peroxidase, the main conjugates are 7.7% for IE, 2.1% for E, 0.7% for AIE, and 0.2% for MIE. IE, which is a potent sensitizer in vivo, produces the greatest amount of conjugates while MIE, which is negative in vivo, produces almost no conjugates.
CONCLUSIONS:
AIE and E, both mild sensitizers in vivo, produce less conjugates than IE. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)