| Cell Research: |
| Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(3):455-60. | | Betulin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines expression through activation STAT3 signaling pathway in human cardiac cells.[Pubmed: 25720718] | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is an important regulator of cardiac survival pathways. Decreased expression or activity of STAT3 in patients with end-stage heart failure demonstrated a clinical relevance of STAT3 in cardiac diseases. Betulin, a pentacyclic triterpene, has drawn extensive attention towards its beneficial effects. However, little is known about its roles in cardiac cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effects of Betulin on the pro-inflammatory processes in human cardiac AC16 cells. Genes expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of NF-κB signaling were analyzed. Besides, levels of phosphorylated STAT3 and its down-stream target genes were measured to evaluate the activation of STAT3. Finally, STAT3 inhibitor and small interfering RNA (siRNA) oligos were used to determine the roles of STAT3 in AC16 cells treated with Betulin.
Our results revealed that Betulin inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokines expression and NF-κB signaling activation through STAT3 signaling. Besides, Betulin treatment also induced the expression of Bcl-xL, an anti-apoptotic downstream effector of STAT3.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results, for the first time, uncovered the cardioprotective roles of Betulin, which may be useful to reduce the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. | | Toxicology. 2011 Feb 27;280(3):152-63. | | Betulin and betulinic acid attenuate ethanol-induced liver stellate cell activation by inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS), cytokine (TNF-α, TGF-β) production and by influencing intracellular signaling.[Pubmed: 21172400] | Liver fibrosis has been reported to be inhibited in vivo by oleanolic and ursolic acids. However, the mechanisms of the action of those triterpenoids are poorly understood. In this study, we aimed to determine the antifibrotic potential of other triterpenes, Betulin and Betulinic acid, and to characterize their influence on the signal transduction pathways involved in ethanol-activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Investigated was the influence of preincubation of rat HSCs with Betulin and Betulinic acid, at non-toxic concentrations, on ethanol-induced toxicity, migration, and several markers of HSC activation such as smooth muscle α-actin (α-SMA) and procollagen I expression, release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cytokines: tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and tumor growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and production of metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2). To assess the mechanism of the action of those triterpenes, intracellular signals such as nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) induced by ethanol were examined.
In vitro, Betulin, but not Betulinic acid, protected HSCs against ethanol toxicity. However, both Betulin and Betulinic acid inhibited the production of ROS by HSCs treated with ethanol and inhibited their migration as well as ethanol-induced TNF-α, and TGF-β1, production. Betulin and Betulinic acid down-regulated ethanol-induced production of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. Betulin and Betulinic acid, also decreased ethanol-induced activity of MMP-2. In ethanol-induced HSCs, Betulin inhibited the activation of the p38 MAPK and the JNK transduction pathways, while Betulinic acid inhibited the JNK transduction pathway only. They also significantly inhibited phosphorylation of IκB and Smad 3 and attenuated the activation of TGF-β1 and NFκB/IκB transduction signaling.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that Betulin and Betulinic acid inhibited ethanol-induced activation of HSCs on different levels, acting as antioxidants, inhibitors of cytokine production, and inhibitors of TGF-β, and NFκB/IκB transduction signaling. Betulin was also inhibitor of both JNK and p38 MAPK signal transduction, while Betulinic acid inhibited only JNK. The remarkable inhibition of several markers of HCS activation makes triterpenes, especially Betulin, promising agents for anti-fibrotic combination therapies. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
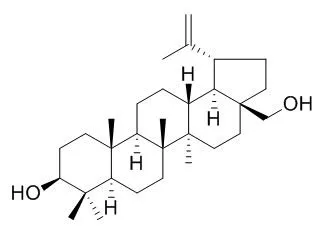
| Drug Deliv. 2014 Sep;21(6):467-79. | | Preparation and characterization of betulin nanoparticles for oral hypoglycemic drug by antisolvent precipitation.[Pubmed: 24479653] | Betulin, a kind of small molecular compound, was reported that has hypoglycemic effect. Due to its low aqueous solubility and high permeability, Betulin has low and variable oral bioavailability.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work, Betulin nanoparticles were thus prepared by antisolvent precipitation for accelerating dissolution of this kind of poorly water-soluble drugs. Ethanol was used as solvent and deionized water was used as antisolvent. The effects of various experimental parameters on the mean particle size (MPS) of nanocrystallization Betulin were investigated. The MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension basically remain unchanged when precipitation time was within 60 min and then increased from 304 nm to 505 nm later. However, the MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension decreased with increased Betulin solution concentration. On the contrary, the MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension decreased along with the increase of temperature. Stirring intensity and the speed ratio of solvent adding into antisolvent had no significant influences on the MPS of Betulin nanoparticles suspension. Betulin nanoparticles suspension with a MPS of approximately 110 nm was achieved under the optimal precipitation conditions. FTIR, Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) were used to analyze the characteristic of Betulin nanoparticles powder. These results show that Betulin nanoparticles powder has the same chemical structure as raw drug, but a smaller size and lower crystallinity. The dissolution rate and solubility of Betulin nanoparticles powder were separately 3.12 and 1.54 times of raw drug. The bioavailability of Betulin nanoparticles powder increased 1.21 times compared with raw Betulin.
CONCLUSIONS:
The result of in vivo evaluation on diabetic animals demonstrates that the Betulin nanoparticles powder show an excellent hypoglycemic effect compared with raw Betulin. In addition, the residual ethanol is less than the ICH (International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human) limit for class 3 solvents of 5000 ppm or 0.5% for solvents. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)