| Description: |
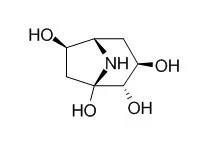
Calystegine B1 is a noncompetitive inhibitor of rice alpha-glucosidase, with a Ki value of 0.9 +/- 0.1 microM. Calystegine B1 and Calystegine C1 are potent competitive inhibitors of the bovine, human, and rat beta-glucosidase activities, with Ki values of 150, 10, and 1.9 microM. |
| In vitro: |
| Carbohydr Res. 1997 Nov 10;304(2):173-8. | | Enzymatic synthesis of the glycosides of calystegines B1 and B2 and their glycosidase inhibitory activities.[Pubmed: 9449768] |
Several glycosides of Calystegine B1 and calystegine B2 were synthesized by use of rice alpha-glucosidase and the whole cells of Rhodotorula lactosa, and their glycosidase inhibitory activities were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Incubation of mixture of Calystegine B1 and maltose with rice alpha-glucosidase gave 3-O-alpha-D-glucopyranosylCalystegine B1 (2, 11.3%). An enzymatic beta-transglucosylation reaction of Calystegine B1 or calystegine B2 with cellobiose using the whole cells of R. lactosa gave 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylCalystegine B1 (1) (0.9%) or 4-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylcalystegine B2 (3, 11.2%), respectively, while similar beta-transgalactosylation of calystegine B2 from lactose gave 4-O-beta-D-galactopyranosylcalystegine B2 (4, 10.1%).
CONCLUSIONS:
The glycosylation of Calystegine B1 and calystegine B2 markedly decreased or abolished their inhibition against beta-glucosidase, alpha- or beta-galactosidase. | | Glycobiology. 1997 Dec;7(8):1085-8. | | The effects of calystegines isolated from edible fruits and vegetables on mammalian liver glycosidases.[Pubmed: 9455909] | The polyhydroxylated nortropane alkaloids called calystegines occur in many plants of the Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae, and Moraceae families. Certain of these alkaloids exhibit potent inhibitory activities against glycosidases and the recently demonstrated occurrence of calystegines in the leaves, skins, and sprouts of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), and in the leaves of the eggplant (S. melongena), has raised concerns regarding the safety of these vegetables in the human diet.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We have surveyed the occurrence of calystegines in edible fruits and vegetables of the families Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae, and Moraceae by GC-MS. Calystegines A3, Calystegine B1, Calystegine B2, and Calystegine C1 were detected in all the edible fruits and vegetables tested; sweet and chili peppers, potatoes, eggplants, tomatoes, Physalis fruits, sweet potatoes, and mulberries. Calystegine B1 and Calystegine C1 were potent competitive inhibitors of the bovine, human, and rat beta-glucosidase activities, with Ki values of 150, 10, and 1.9 microM, respectively for B1 and 15, 1.5, and 1 microM, respectively, for C1. Calystegine B2 was a strong competitive inhibitor of the alpha-galactosidase activity in all the livers.
CONCLUSIONS:
Human beta-xylosidase was inhibited by all four nortropanes, with calystegine C1 having a Ki of 0.13 microM. Calystegine A3 and Calystegine B2 selectively inhibited the rat liver beta-glucosidase activity. The potent inhibition of mammalian beta-glucosidase and alpha-galactosidase activities in vitro raises the possibility of toxicity in humans consuming large amounts of plants that contain these compounds. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)