| Description: |
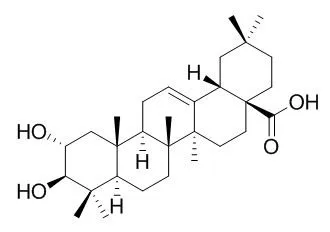
Crategolic acid(Maslinic acid) has neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti- osteoporosis, cytotoxic and antiviral activities, it suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NF-κB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathways , and has beneficial effects on hypoxic neurons by suppressing iNOS activation.Crategolic acid as a feed additive to stimulate growth and hepatic protein-turnover rates in rainbow trout ( Onchorhynchus mykiss ).
|
| In vitro: |
| Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1992 Feb;40(2):401-5. | | Studies on differentiation-inducing activities of triterpenes.[Pubmed: 1606636] | Differentiation-inducing activity of over 180 extracts of crude drugs and plants was tested using mouse myeloid leukemia cell line (M1).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanol extracts of clove (Syzygium aromaticum Merrill et Perry, Myrtaceae) showed remarkable induction of differentiation of M1 cells into macrophage-like cells. From the extract, oleanolic acid (1) and Crategolic acid (2) were isolated as the active components. We also tested other triterpenes, such as oleananes, ursanes and dammaranes, to investigate the structure-activity relationship. Some triterpene aglycones showed differentiation-inducing activity, but triterpene glycosides showed little activity. Furthermore, the differentiation-inducing activity of these triterpene compounds was tested against human acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60). | | Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Feb 1;17(3):1139-45. | | Solution- and solid-phase synthesis and anti-HIV activity of maslinic acid derivatives containing amino acids and peptides.[Pubmed: 19135380 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Maslinic acid (1,Crategolic acid,) has been coupled at C-28 with several alpha- and omega-amino acids by using solution- and solid-phase synthetic procedures. Twelve derivatives (2-13) with a single amino acid residue were prepared in solution phase, whereas a dipeptide (14), a tripeptide (15), and a series of conjugate dipeptides (16-24) were synthesized in solid phase. The anti-HIV activity of these compounds was assessed on MT-2 cells infected with viral clones carrying the luciferase gene as a reporter.
CONCLUSIONS:
While in maslinic acid (1) were present both cytotoxic and antiviral activities, only the derivatives 13 and 24 showed anti-HIV-1 activity and therefore represent a novel class of anti-HIV-1 compounds. | | J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26(3):644-56. | | Maslinic acid suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss by regulating RANKL-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 20814972 ] | Activation of NF-κB and MAPK/activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling pathways by receptor activator NF-κB ligand (RANKL) is essential for osteoclast activity. Targeting NF-κB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling to modulate osteoclast activity has been a promising strategy for osteoclast-related diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study we examined the effects of maslinic acid (Crategolic acid,MA), a pentacyclic triterpene acid that is widely present in dietary plants, on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis, osteoclast function, and signaling pathways by in vitro and in vivo assay systems. In mouse bone marrow monocytes (BMMs) and RAW264.7 cells, MA inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in a dose-dependent manner within nongrowth inhibitory concentration, and MA decreased osteoclastogenesis-related marker gene expression, including TRACP, MMP9, c-Src, CTR, and cathepsin K. Specifically, MA suppressed osteoclastogenesis and actin ring formation at early stage. In ovariectomized mice, administration of MA prevented ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity. At molecular levels, MA abrogated the phosphorylation of MAPKs and AP-1 activity, inhibited the IκBα phosphorylation and degradation, blocked NF-κB/p65 phosphorylation, nuclear translocation, and DNA-binding activity by downregulating RANK expression and blocking RANK interaction with TRAF6.
CONCLUSIONS:
Together our data demonstrate that MA suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NF-κB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathways and that MA is a promising agent in the treatment of osteoclast-related diseases such as osteoporosis. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Mol Nutr Food Res . 2016 Feb;60(2):399-409. | | Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of pentacyclic triterpenoids maslinic acid through NF-κB inactivation[Pubmed: 26499467] | | Abstract
Scope: Consumption of olives (Olea europaea L.), including table olives and oil, is associated with low incidence of inflammation-related diseases. In this study, the effects of maslinic acid (MA), the main constituent of olive pomace, on the expression of genes and proteins involved in inflammatory activity in RAW 264.7 cells were investigated. Furthermore, the effect of MA on carrageenan-induced paw edema and collagen antibody induced arthritis in mice was determined.
Methods and results: We confirmed the suppressive effects of MA on LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor α production and on the expression of inflammatory response associated genes in RAW 264.7 cells. We also clarified the suppressive effect of MA on LPS-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation as well as the phosphorylation of IκB-α. Furthermore, MA (200 mg/kg in the edema model or 100 mg/kg in the arthritis model) exerted anti-inflammatory and antiarthritis effects as shown by the suppression of paw edema, arthritis score, inflammatory cells, and destruction of synovium in knee joints.
Conclusion: Olive products containing MA are useful as a new preventive and therapeutic food ingredient for inflammatory and arthritic diseases.
Keywords: Arthritis; Inflammation; Locomotive syndrome; Maslinic acid; Olive fruit. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)