| Kinase Assay: |
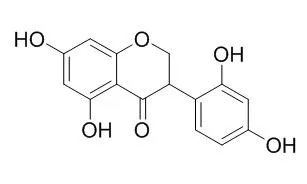
| J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 May;18(5):874-9. | | Inhibitory effect of dalbergioidin isolated from the trunk of Lespedeza cyrtobotrya on melanin biosynthesis.[Pubmed: 18633284] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Tyrosinase is a key enzyme for melanin biosynthesis, and hyperpigmentation disorders are associated with abnormal accumulation of melanin pigments, which can be reduced by treatment with depigmenting agents. The methanol extract of Lespedeza cyrtobotrya MIQ showed inhibitory activity against mushroom tyrosinase. The active compound was purified from the methanol extract of L cyrtobotrya, followed by several chromatographic methods, and identified as Dalbergioidin (DBG) by spectroscopic methods.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results showed that DBG exhibited tyrosinase inhibitory activity with an IC50 of 20 mM. The kinetic analysis tyrosinase inhibition revealed that DBG acted as noncompetitive inhibitor. In addition, DBG showed a melanin biosynthesis inhibition zone in the culture plate of Streptomyces bikiniensis that has commonly been used as an indicator organism. Furthermore, 27 mM DBG decreased more than 50% of melanin contents on the pigmentation using immortalized mouse melanocyte, melan-a cell. | | Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;390(7):711-720. | | Dalbergioidin (DAL) protects MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells against H2O2-induced cell damage through activation of the PI3K/AKT/SMAD1 pathway.[Pubmed: 28374099 ] |
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a pivotal pathogenic factor in the development of osteoporosis. Dalbergioidin (DAL) can be isolated from Uraria crinite, an edible herb used as a natural food for childhood skeletal dysplasia. Recent research has implicated DAL as having an antiosteoporosis effect, although the mechanism of this is unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We used an effective oxidative stress model, induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells, to investigate the protective effects of DAL in osteoporosis and the underlying molecular mechanisms. The results indicated that treatment with DAL maintained redox balance, reduced MC3T3-E1 cell apoptosis, improved alkaline phosphatase activity, and elevated the osteogenic-related protein expression of Runx2, Osterix, and BMP2 against oxidative damage induced by H2O2. The potential molecular mechanism involved in the protective effect of DAL against H2O2-induced cell death in MC3T3-E1 cells may lie in the activation of the PI3K/AKT/SMAD1 cell signal pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results indicated that the potential protective effects of DAL against osteoporosis were linked to a reduction in oxidative damage, suggesting that DAL may be useful in bone metabolism diseases, particularly osteoporosis. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5147571. | | Dalbergioidin Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Renal Fibrosis by Suppressing the TGF-β Signal Pathway.[Pubmed: 28100935] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effect of Dalbergioidin (DAL), a well-known natural product extracted from Uraria crinita, on doxorubicin- (DXR-) induced renal fibrosis in mice. The mice were pretreated for 7 days with DAL followed by a single injection of DXR (10 mg/kg) via the tail vein. Renal function was analyzed 5 weeks after DXR treatment. DXR caused nephrotoxicity. The symptoms of nephrotic syndrome were greatly improved after DAL treatment. The indices of renal fibrosis, the phosphorylation of Smad3, and the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), fibronectin, collagen III (Col III), E-cadherin, TGF-β, and Smad7 in response to DXR were all similarly modified by DAL.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present findings suggest that DAL improved the markers for kidney damage investigated in this model of DXR-induced experimental nephrotoxicity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)