| Structure Identification: |
| Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Mar;38(5):703-8. | | Chemical constituents from leaves of Nelumbo nucifera.[Pubmed: 23724680] | To study the chemical constituents, twenty-seven compounds were isolated from the 70% ethanol extract from leaves of Nelumbo nucifera by modern chromatographic techniques.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
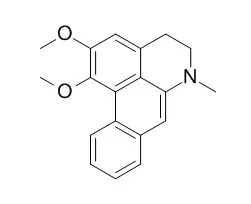
Their structures were identified as 10-octacosanol (1), beta-sitosterol (2), 1-undecanol (3), 1-eicosanol (4), daucosterol (5), 6'-hydroxy-4,4'-dimethoxychalcone (6), 3,7,8-trimethoxy-1-hydroxy-xanthone (7), rhamnetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (8), chrysoeriol-7-O-beta-D-glucoside (9), quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (10), quercetin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl (11), hyperoside (12), quercetin-3-O-rutinoside (13), astragalin (14), isorhamnetin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1--> 6)-[alpha-D-lyxopyranosyl-(1 --> 2) -beta-D-glucopyranoside] (15), isorhamnetin-3-O-alpha-D-lyxopyranosyl-(1 --> 2) -beta-D-glucopyranoside (16), isorhamnetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (17), isorhamnetin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 --> 6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (18), quercetin (19), kaempferol (20), Dehydronuciferine (21), roemerine (22), stigmast-7-en-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (23), stigmast-7-en-3beta-ol (24), and benzene-1,2-diol (25) on the basis of spectral data analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1, 6, 7, 8, 24 and 25 were isolated from this plant for the first time, and compounds 15-18 were isolated from the leaves for the first time. Compounds 6, 8, 10, 11, 13 and 15 showed inhibitory activities against beta amyloid (1-42) by A-beta aggregation method with inhibition rates of (63.99 +/- 24.29)%, (79.61 +/- 4.49)%, (49.96 +/- 12.61)%, (101.19 +/- 8.19)%, (88.41+/-6.76)% and (72.48 +/- 8.97)%, respectively. | | Medicinal Chemistry Research, 2014, 23(6):3178-3186. | | Synthesis and structure-Activity relationship of nuciferine derivatives as potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors[Reference: WebLink] | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) are currently the best available pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer patients, but because of bioavailability issues, there is still great interest in discovering better AChEIs. The aporphine alkaloid is an important class of natural products, which shows diverse biological activity, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To find new lead AChEIs compounds, eight aporphine alkaloids were synthesized by O-dealkylation, N-dealkylation, and ring aromatization reactions using nuciferine as raw material. The anti-acetylcholinesterase activity of synthesized compounds was measured using modified Ellman’s method. The results showed that some synthesized compounds exhibited higher affinity to AChE than the parent compound nuciferine. Among these compounds, 1,2-dihydroxyaporphine (2) and Dehydronuciferine (5) were the most active compounds (IC50 = 28 and 25 μg/mL, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS:
Preliminary analysis of structure–activity relationships suggested that aromatization of the C ring, the presence of the alkoxyl group at C1 and the hydroxy group at C2 position as well as the alkyl substituent at the N atom were favorable to the acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Molecular docking was also applied to predict the binding modes of compounds 1, 2, and 9 into the huperzine A binding site of AChE. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)