| Structure Identification: |
| Nat Prod Commun. 2009 Jul;4(7):907-10. | | Phytochemical characterization of the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa grown in U.S.A.[Pubmed: 19731590] | Mitragyna speciosa (Rubiaceae) has traditionally been used in the tropical regions of Asia, Africa and Indonesia as a substitute for opium. Indole alkaloids are the most common compounds that have been isolated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
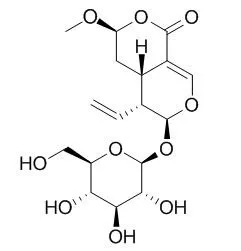
We investigated the constituents of the leaves of M. speciosa that was grown at the University of Mississippi. Several alkaloids were isolated, including ajmalicine, corynantheidine, isomitraphylline, mitraphylline, paynantheine, isocorynantheidine, 7-hydroxymitragynine and mitragynine, but their percentages were lower than those in a commercial Thai sample of "kratom". In addition, we isolated the flavonoid epicatechin, a saponin daucosterol, the triterpenoid saponins quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-quinovopyranoside, quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, as well as several glycoside derivatives including 1-O-feruloyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside, benzyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 3-oxo-alpha-ionyl-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, roseoside, vogeloside, and Epivogeloside.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of the last group of compounds having been isolated from a Mitragyna species. Biological studies are currently underway to test these compounds for opioid activity.
|
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)