| In vitro: |
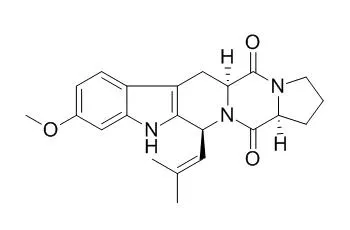
| Cancer Res. 2000 Jan 1;60(1):47-50. | | Fumitremorgin C reverses multidrug resistance in cells transfected with the breast cancer resistance protein.[Pubmed: 10646850] | Fumitremorgin C (FTC) is a potent and specific chemosensitizing agent in cell lines selected for resistance to mitoxantrone that do not overexpress P-glycoprotein or multidrug resistance protein.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The gene encoding a novel transporter, the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), was recently found to be overexpressed in a mitoxantrone-selected human colon cell line, S1-M1-3.2, which was used to identify FTC. Because the drug-selected cell line may contain multiple alterations contributing to the multidrug resistance phenotype, we examined the effect of FTC on MCF-7 cells transfected with the BCRP gene.
CONCLUSIONS:
We report that FTC almost completely reverses resistance mediated by BCRP in vitro and is a pharmacological probe for the expression and molecular action of this transporter. | | Natural Product Sciences, 2007,13(3):251-4. | | 12,13-Dihydroxyfumitremorgin C, Fumitremorgin C, and Brevianamide F, Antibacterial Diketopiperazine Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Pseudallescheria sp.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Dioxopiperazine alkaloids, 12R,13S-dihydroxyFumitremorgin C (1), Fumitremorgin C (2), and brevianamide F (3), were isolated from the marine-derived fungus Pseudallescheria, and the absolute stereostructures of compounds 1 - 3 were elucidated on the basis of chemical and physicochemical evidence.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1 - 3 showed an antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant S. aureus, and multidrug-resistant S. aureus. The MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of compounds 1 - 3 were 125 ug/ml for all strains. | | Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(16):1545-50. | | Cytotoxic compounds from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. recovered from the sediments of the Brazilian coast.[Pubmed: 25532964 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A fungal strain of Aspergillus sp. (BRF 030) was isolated from the sediments collected in the northeast coast of Brazil, and the cytotoxic activity of its secondary metabolites was investigated against HCT-116 tumour cell line. The cytotoxicity-guided fractionation of the extracts from this fungus cultured in potato-dextrose-sea water for 14 days at room temperature yielded the hetero-spirocyclic γ-lactams pseurotin A (1), pseurotin D (2) and pseurotin FD-838 (7), the alkaloids Fumitremorgin C (5), 12,13-dihydroxy Fumitremorgin C (6), methylsulochrin (4) and bis(dethio)bis(methylthio)gliotoxin (3). Among them, Fumitremorgin C (5) and 12,13-dihydroxy Fumitremorgin C (6) were the most active.
The cytotoxic activities of the extracts from Aspergillus sp. grown from 7 to 28 days were investigated, and they were associated with the kinetic production of the compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most active extracts (14 and 21 days) were those with the highest relative concentrations of the compounds Fumitremorgin C (5) and 12,13-dihydroxy Fumitremorgin C (6). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)