| In vitro: |
| Biol Pharm Bull. 2006 Apr;29(4):838-40. | | Hepatoprotective compounds of the roots of Cudrania tricuspidata on tacrine-induced cytotoxicity in Hep G2 cells.[Pubmed: 16595932] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The bioassay-guided fractionation of the MeOH extract of the root barks of Cudrania tricuspidata furnished three hepatoprotective compounds, gerontoxanthone A (2), cudraflavone B (4), Gericudranin E (5), together with four prenylated xanthones, cudraxanthone B (3), isocudraxanthone K (6), cudraxanthone C (7), cudraxanthone H (8), and a prenylated flavanone, euchrestaflavanone C (1).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 4 and 5 showed significant hepatoprotective effects with the EC50 values of 37.39+/-0.4 and 39.87+/-0.7 microM, respectively, and compound 2 showed moderate hepatoprotective effect with an EC50 value of 125.9+/-1.5 microM, against tacrine-induced cytotoxicity in Hep G2 cells.
Silybin as positive control showed an EC50 value of 84.76+/-0.5 microM. Isocudraxanthone K (6) is a new compound. | | Natural Product Sciences, 2010, 16(2):75-79. | | Monoamine oxidase inhibitory flavonoids from the root bark of Cudrania tricuspidata.[Reference: WebLink] |
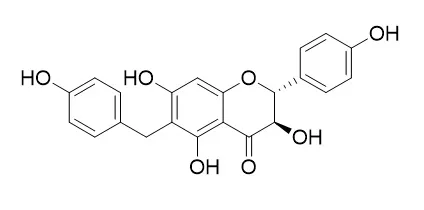
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new benzylated flavonoids, 5,7,4′-trihydroxy-6-p- hydroxybenzylflavanone (1) and 5,7,4′-trihydroxy-6,8-di-p- hydroxybenzylflavanone (2) together with six known flavonoids, kaempferol (3), artocarpesin (4), cycloartocarpesin (5), cudraflavone D (6), Gericudranin E (7), and leachianone G (8) have been isolated from the root bark of Cudrania tricuspidata. The structures of 1 and 2 were characterized based on spectroscopic data including 1D- and 2D-NMR. All the isolates were evaluated for their inhibitory effects of monoamine oxidase (MAO).
CONCLUSIONS:
Among them, kaempferol (3), artocarpesin (4), and cudraflavone D (6) showed moderate inhibitory effects with IC50 values of 82.3, 30.8, and 71.8 μM, respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)