| In vitro: |
| Phytochemistry. 2017 Mar;135:128-134. | | Phenolic constituents from the root bark of Morus alba L. and their cardioprotective activity in vitro.[Pubmed: 27974159 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
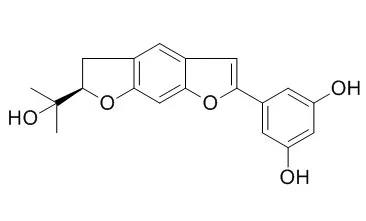
A flavanone C-glycoside, steppogenin-5'-C-β-D-glucopyranoside, six prenylated 2-arylbenzofuran derivatives, Moracin O-3″-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, Moracin O-3'-O-β-D-xylopyranoside, moracin P-2″-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, moracin P-3'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, moracin P-3'-O-α-L-arabinopyranoside and moracin P-3'-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)]-α-L-arabinopyranoside, two phenolic acids, 2,4-dihydroxy-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl) benzoic acid and 2,4-dihydroxy-5-(3,4-dihydroxybenzyl) benzoic acid, as well as three known compounds, moracinoside C, Moracin O, and moracin P were isolated from the root bark of Morus alba L. Their structures were ascertained on the basis of spectroscopic evidence. The protective effects of the compounds against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in H9c2 cells was investigated in vitro.
CONCLUSIONS:
Of all of the isolated compounds, moracin P-3'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, Moracin O and moracin P had a strong protective influence against doxorubicin-induced cell death with EC50 values of 9.5 ± 2.6, 4.5 ± 1.3, and 8.8 ± 2.4 μM, respectively. | | Molecules. 2017 Feb 8;22(2). | | Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives from Cortex Mori Radicis, and Their Neuroprotective and Analgesic Activities Mediated by mGluR₁.[Pubmed: 28208727 ] | Four new benzofuran-type stilbene glycosides and 14 known compounds including 8 benzofuran-type stilbenes and 6 flavonoids were isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine, Cortex Mori Radicis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The new compounds were identified as (9R)-moracin P 3'-O-α-l-arabinopyranoside (1), (9R)-moracin P 9-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (2), (9R)-moracin P 3'-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (3), and (9R)-Moracin O 10-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (4) based on the spectroscopic interpretation and chemical analysis. Three benzofuran-type stilbenes, Moracin O (5), R (7), and P (8) showed significant neuroprotective activity against glutamate-induced cell death in SK-N-SH cells. In addition, Moracin O (5) and P (8) also demonstrated a remarkable inhibition of the acetic acid-induced pain.
CONCLUSIONS:
The molecular docking with metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR₁) results indicated that these neuroprotective benzofuran-type stilbenes might be the active analgesic components of the genus Morus, and acted by mediating the mGluR₁ pathway. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)