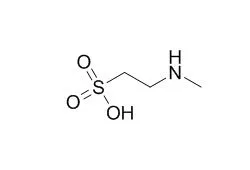
| Structure Identification: |
| Microbiology. 2006 Apr;152(Pt 4):1179-86. | | The sulfonated osmolyte N-methyltaurine is dissimilated by Alcaligenes faecalis and by Paracoccus versutus with release of methylamine.[Pubmed: 16549680] | Selective enrichments yielded bacterial cultures able to utilize the osmolyte N-Methyltaurine as sole source of carbon and energy or as sole source of fixed nitrogen for aerobic growth. Strain MT1, which degraded N-Methyltaurine as a sole source of carbon concomitantly with growth, was identified as a strain of Alcaligenes faecalis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Stoichiometric amounts of methylamine, whose identity was confirmed by matrix-assisted, laser-desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, and of sulfate were released during growth. Inducible N-Methyltaurine dehydrogenase, sulfoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase (Xsc) and a sulfite dehydrogenase could be detected. Taurine dehydrogenase was also present and it was hypothesized that taurine dehydrogenase has a substrate range that includes N-Methyltaurine. Partial sequences of a tauY-like gene (encoding the putative large component of taurine dehydrogenase) and an xsc gene were obtained by PCR with degenerate primers. Strain N-MT utilized N-Methyltaurine as a sole source of fixed nitrogen for growth and could also utilize the compound as sole source of carbon. This bacterium was identified as a strain of Paracoccus versutus. This organism also expressed inducible N-Methyltaurine dehydrogenase, Xsc and a sulfite dehydrogenase.
CONCLUSIONS:
The presence of a gene cluster with high identity to a larger cluster from Paracoccus pantotrophus NKNCYSA, which is now known to dissimilate N-Methyltaurine via Xsc, allowed most of the overall pathway, including transport and excretion, to be defined. N-Methyltaurine is thus another compound whose catabolism is channelled directly through sulfoacetaldehyde. | | Physiol Biochem Zool. 2000 Sep-Oct;73(5):629-37. | | Hypotaurine, N-methyltaurine, taurine, and glycine betaine as dominant osmolytes of vestimentiferan tubeworms from hydrothermal vents and cold seeps.[Pubmed: 11073799] | Organic osmolytes, solutes that regulate cell volume, occur at high levels in marine invertebrates. These are mostly free amino acids such as taurine, which are "compatible" with cell macromolecules, and methylamines such as trimethylamine oxide, which may have a nonosmotic role as a protein stabilizer, and which is higher in many deep-sea animals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To better understand nonosmotic roles of osmolytes, we used high-performance liquid chromatography and (1)H-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to analyze vestimentiferans (vestimentum tissue) from unusual marine habitats. Species from deep hydrothermal vents were Riftia pachyptila of the East Pacific Rise (2,636 m) and Ridgeia piscesae of the Juan de Fuca Ridge (2,200 m). Species from cold hydrocarbon seeps were Lamellibrachia sp. and an unnamed escarpid species from subtidal sediment seeps (540 m) off Louisiana and Lamellibrachia barhami from bathyal tectonic seeps (1,800-2,000 m) off Oregon. Riftia were dominated by hypotaurine (152 mmol/kg wet wt), an antioxidant, and an unidentified solute with an NMR spectrum consistent with a methylamine. Ridgeia were dominated by betaine (N-trimethylglycine; 109 mmol/kg), hypotaurine (64 mmol/kg), and taurine (61 mmol/kg). The escarpids were dominated by taurine (138 mmol/kg) and hypotaurine (69 mmol/kg). Both Lamellibrachia populations were dominated by N-Methyltaurine (209-252 mmol/kg), not previously reported as a major osmolyte, which may be involved in methane and sulfate metabolism.
CONCLUSIONS:
Trunk and plume tissue of the Oregon Lamellibrachia were nearly identical to vestimentum in osmolyte composition. The methylamines may also stabilize proteins against pressure; they were significantly higher in the three deeper-dwelling groups. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)