| Description: |
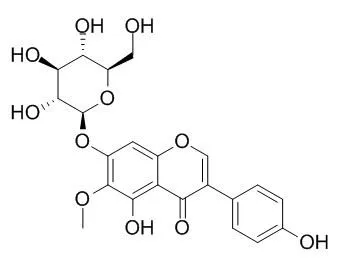
Tectoridin, an lens aldose reductase inhibitor, has several pharmacological effects including hypoglycemic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotectivy. It possesses a estrogenic and thyroid hormone-like agent by activating estrogen and thyroid hormone receptors, it also has inhibition on prostaglandin E2 production and cyclooxygenase-2 induction. |
| In vitro: |
| Phytomedicine. 2014 Apr 15;21(5):602-6. | | Tectoridin from Maackia amurensis modulates both estrogen and thyroid receptors.[Pubmed: 24252334] | The stem bark of Maackia amurensis has been used as folk medicine for the treatment of cancer, cholecystitis, arthritis, and hyperthyroidism in females. In this study we examined the effects of the ethyl acetate fraction obtained from the 70% ethanol extract of M. amurensis and Tectoridin, an active constituent isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction on thyroid and estrogen hormone activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of the ethanolic extract of M. amurensis stem bark on thyroid hormone activity was evaluated using thyroid hormone responsive-luciferase assay. We isolated Tectoridin from the ethyl acetate fraction using a recrystallization method. T-screen assays were used to confirm thyroid hormone activity. The estrogenic activity of the ethyl acetate fraction of M. amurensis and Tectoridin was evaluated by estrogen responsive-luciferase assay and estrogen receptor alpha regulation as compared to 17β-estradiol.
Both the ethyl acetate fraction and Tectoridin activated thyroid-responsive reporters and increased thyroid hormone-dependent proliferation of rat pituitary GH3 cells, indicating modulation of thyroid hormone receptors. In parallel, the estrogenic activity of the fraction and Tectoridin were characterized in a transient transfection system using estrogen-responsive luciferase plasmids in MCF-7 cells. The ethyl acetate fraction and Tectoridin activated reporter gene expression and decreased the estrogen receptor protein level.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data indicate that Tectoridin acts as a weak phytoestrogen as well as a thyroid hormone-like agent by activating both estrogen and thyroid hormone receptors. | | Mol Cells. 2009 Mar 31;27(3):351-7. | | Tectoridin, a poor ligand of estrogen receptor alpha, exerts its estrogenic effects via an ERK-dependent pathway.[Pubmed: 19326083 ] | Phytoestrogens are the natural compounds isolated from plants, which are structurally similar to animal estrogen, 17beta-estradiol. Tectoridin, a major isoflavone isolated from the rhizome of Belamcanda chinensis. Tectoridin is known as a phytoestrogen, however, the molecular mechanisms underlying its estrogenic effect are remained unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study we investigated the estrogenic signaling triggered by Tectoridin as compared to a famous phytoestrogen, genistein in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Tectoridin scarcely binds to ER alpha as compared to 17beta-estradiol and genistein. Despite poor binding to ER alpha, Tectoridin induced potent estrogenic effects, namely recovery of the population of cells in the S-phase after serum starvation, transactivation of the estrogen response element, and induction of MCF-7 cell proliferation. The Tectoridin-induced estrogenic effect was severely abrogated by treatment with U0126, a specific MEK1/2 inhibitor. Tectoridin promoted phosphorylation of ERK1/2, but did not affect phosphorylation of ER alpha at Ser(118). It also increased cellular accumulation of cAMP, a hallmark of GPR30-mediated estrogen signaling.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data imply that Tectoridin exerts its estrogenic effect mainly via the GPR30 and ERK-mediated rapid nongenomic estrogen signaling pathway. This property of Tectoridin sets it aside from genistein where it exerts the estrogenic effects via both an ER-dependent genomic pathway and a GPR30-dependent nongenomic pathway. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Apr;97(4):541-4. | | Hepatoprotective effect of tectoridin and tectorigenin on tert-butyl hyperoxide-induced liver injury.[Pubmed: 15821336] | To clarify the hepatoprotective effects of Tectoridin and tectorigenin from Puerariae Flos, their effects on tert-butyl hyperoxide (t-BHP)-injured HepG2 cells and mice were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
When tectorigenin at a dose of 50 mg/kg was intraperitoneally administered to mice injured by t-BHP, it significantly inhibited the increase the activities of plasma ALT and AST by 39% and 41%, respectively, in the t-BHP-treated group. The inhibitory effect of tectorigenin is much more potent than that of a commercially available dimethyl diphenyl bicarboxylate. Orally administered Tectoridin showed hepatoprotective activity. However, when Tectoridin was intraperitoneally administrated to mice, no hepatoprotective activity was observed. Tectorigenin also protected against the cytotoxicity of HepG2 cells induced by t-BHP. This protection may have originated from the inhibition of apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Tectorigenin may be hepatoprotective and Tectoridin should be a prodrug that is transformed to tectorigenin. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)